In the world of machining and metalworking, selecting the right tool material can make all the difference in productivity, precision, and cost-effectiveness. Two of the most common materials used in cutting tools are carbide and High-Speed Steel (HSS). Each has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different applications. This comprehensive guide will explore the differences between carbide and HSS tools across various applications, helping you make informed decisions for your specific needs.
Understanding HSS VS Carbide
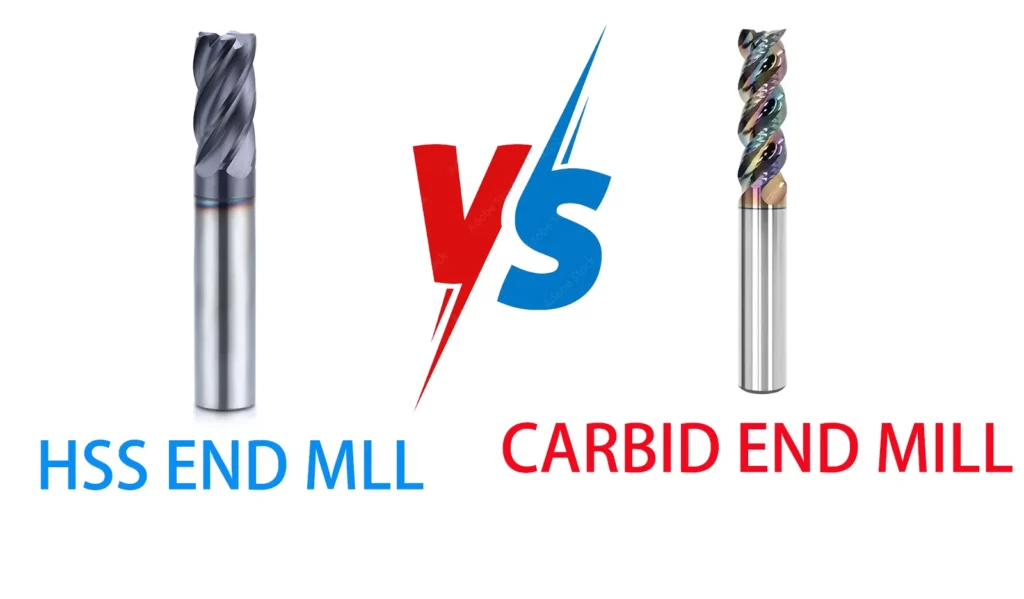

Before diving into specific tool types, it’s essential to understand the basic properties of carbide and HSS.
Carbide, also known as cemented carbide or tungsten carbide, is a composite material made of tungsten carbide particles bonded together with a metallic binder, usually cobalt. It’s known for its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and ability to maintain a sharp cutting edge at high temperatures.
High-Speed Steel (HSS) is an alloy steel containing significant amounts of tungsten, molybdenum, vanadium, and chromium. It offers good hardness and toughness, and can withstand higher cutting temperatures than standard carbon steel.
In general, carbide is harder and more wear-resistant than HSS, allowing for higher cutting speeds and longer tool life. However, HSS is tougher and less brittle, making it more resistant to shock and vibration. HSS tools are also typically less expensive than their carbide counterparts.
Carbide Taps vs HSS Taps
When it comes to tapping operations, both carbide and HSS have their place.
Advantages of Carbide Taps
- Higher cutting speeds, leading to increased productivity
- Excellent wear resistance, resulting in longer tool life
- Superior performance in harder materials
- Better thread quality in certain applications
Disadvantages of Carbide Taps
- More expensive than HSS taps
- More brittle and susceptible to breakage if not used properly
- Require more rigid machine setups to prevent chipping
Advantages of HSS Taps
- More forgiving in less rigid setups
- Lower cost, making them economical for smaller production runs
- Easier to resharpen, extending usable life
- Better performance in softer, gummy materials
Disadvantages of HSS Taps
- Lower cutting speeds compared to carbide
- Shorter tool life in abrasive materials
- May struggle with very hard materials
Best Applications
- Use carbide taps for high-volume production, harder materials (>35 HRC), and when superior thread quality is crucial.
- Choose HSS taps for general-purpose tapping, softer materials, and when machine rigidity might be an issue.
Carbide vs HSS Drill Bits
Drill bits are essential in many machining operations, and the choice between carbide and HSS can significantly impact performance.
Carbide Drill Bits
- Offer higher cutting speeds and feed rates
- Provide longer tool life, especially in abrasive materials
- Maintain better hole accuracy and surface finish
- Excel in drilling harder materials
HSS Drill Bits
- More economical for low-volume production
- Less brittle, reducing the risk of breakage in unstable conditions
- Easier to resharpen, often multiple times
- Perform well in a wide range of common materials
Cost Considerations
Carbide drill bits are generally more expensive upfront but can be more cost-effective in high-volume production due to their longer life and higher productivity. HSS bits are more budget-friendly for occasional use or smaller shops.
Suitable Materials and Applications
- Use carbide drill bits for hard metals, composites, and abrasive materials, especially in high-volume production.
- Opt for HSS drill bits for general-purpose drilling in softer metals, wood, and plastics, particularly in low-volume or varied applications.
Carbide vs HSS End Mills
End mills are versatile cutting tools used in milling operations, and the choice between carbide and HSS can greatly affect machining efficiency.
Cutting Speed and Feed Rates
Carbide end mills can operate at significantly higher cutting speeds and feed rates compared to HSS. This translates to faster material removal and increased productivity.
Tool Life and Wear Resistance
Carbide end mills generally offer superior wear resistance, maintaining their cutting edge longer than HSS, especially in harder materials. However, HSS end mills are more resistant to shock and can be more forgiving in less stable machining conditions.
Machining Precision and Surface Finish
Carbide end mills typically produce better surface finishes and maintain tighter tolerances due to their rigidity and resistance to deflection. HSS end mills may require slower speeds to achieve comparable finishes.
Carbide vs HSS Lathe Tools
Lathe tools are crucial for turning operations, and the choice between carbide and HSS depends on various factors.
Cutting Performance on Various Materials
Carbide lathe tools excel in machining harder materials and maintaining consistent performance at high speeds. HSS tools are more versatile and perform well across a wide range of softer to medium-hardness materials.
Heat Resistance and Cooling Requirements
Carbide tools can withstand higher cutting temperatures, often allowing for dry machining or reduced coolant use. HSS tools generally require more cooling to maintain their cutting edge.
Tool Geometry and Versatility
HSS lathe tools can be easily ground to complex geometries, making them versatile for custom profiling. Carbide tools often come in insert form with pre-defined geometries, which can be quickly changed but may offer less customization.
Carbide vs HSS Planer Blades
In woodworking, the choice between carbide and HSS planer blades can affect the quality and efficiency of your work.
Edge Retention and Sharpness
Carbide planer blades maintain their sharp edge much longer than HSS, especially when working with harder woods or composite materials. HSS blades may require more frequent sharpening but can achieve a very keen edge.
Impact Resistance and Durability
HSS planer blades are generally more resistant to impact damage from knots or foreign objects in the wood. Carbide blades are harder but more brittle and may chip if they encounter metal or stones.
Cost-effectiveness for Different Woodworking Needs
For hobbyists or occasional users, HSS blades offer a good balance of performance and affordability. For professional woodworkers or those working with exotic hardwoods, the longer life and consistent performance of carbide blades may justify the higher initial cost.
Carbide vs HSS Wood Lathe Tools
Wood turning requires tools that can handle the unique challenges of shaping wood.
Turning Performance on Different Wood Types
Carbide wood lathe tools excel in turning harder woods and maintaining a consistent edge. HSS tools are more versatile and can be easily sharpened to handle a variety of wood types and turning techniques.
Ease of Sharpening and Maintenance
HSS wood lathe tools can be quickly touched up with a bench grinder or sharpening stone, allowing for frequent resharpening during use. Carbide tools often use replaceable inserts, eliminating the need for sharpening but requiring replacement when dull.
Long-term Value and Investment
While carbide wood lathe tools have a higher upfront cost, their longevity and consistent performance can make them a worthwhile investment for serious woodturners. HSS tools offer lower initial costs and are more suitable for beginners or those who enjoy the process of tool maintenance.
HSS vs Cobalt vs Carbide
When considering cutting tool materials, it’s worth mentioning cobalt steel as an alternative to standard HSS and carbide.
Comparison of Hardness and Wear Resistance
Carbide is the hardest and most wear-resistant, followed by cobalt steel, with HSS being the softest of the three. This translates to longer edge retention for carbide tools, especially in demanding applications.
Heat Tolerance and Cutting Speeds
Carbide tools can withstand the highest cutting temperatures, allowing for the fastest cutting speeds. Cobalt steel offers improved heat resistance over standard HSS, making it suitable for intermediate cutting speeds.
Cost and Performance Trade-offs
HSS tools are the most economical but may require more frequent replacement. Cobalt steel tools offer a middle ground, with improved performance over HSS at a lower cost than carbide. Carbide tools are the most expensive but often provide the best long-term value in high-volume or demanding applications.
Conclusion
Choosing between carbide and HSS tools requires careful consideration of your specific machining needs, budget, and long-term goals. While carbide tools generally offer superior hardness, wear resistance, and cutting speeds, HSS tools provide versatility, impact resistance, and cost-effectiveness for many applications.
Key factors to consider when making your choice include:
- Material being machined
- Production volume
- Machine capabilities and rigidity Initial budget vs. long-term costs
- Required surface finish and tolerances
- Operator skill level and preferences
As machining technology continues to advance, we can expect to see further improvements in both carbide and HSS tool formulations. Additionally, the development of new coating technologies and hybrid materials may further blur the lines between these two stalwart tooling options.
Ultimately, the best choice often depends on finding the right balance between performance and cost for your specific application. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of both carbide and HSS tools, you can make informed decisions that will optimize your machining processes and improve your overall productivity.
What are the differences between HSS and Tungsten carbide?
HSS mainly consists of iron with added carbide-forming alloy elements, while Tungsten carbide mainly consists of Tungsten carbide particles bonded by cobalt. High-speed steel has excellent hot hardness and Tungsten carbide has higher hardness and wear resistance.
What are the different application areas of HSS and Tungsten carbide?
HSS is often used to make cutting tools like drills, end mills, etc. Tungsten carbide is often used for tools in continuous and interrupted cutting like turning, milling, reaming, etc.
What are the pros and cons of HSS and Tungsten carbide respectively?
The pros of HSS are low cost and good machinability; the cons are poorer hardness and wear resistance. The pros of Tungsten carbide are high hardness and wear resistance; the cons are high cost and brittleness.
How do the cutting speeds of HSS and Tungsten carbide compare in machining?
Under the same cutting conditions, Tungsten carbide can have 3-5 times the cutting speed of high-speed steel.
What is the difference in tool life between HSS and Tungsten carbide tools?
Under the same cutting conditions, Tungsten carbide tools can have several times to tens of times more tool life compared to high-speed steel tools.