Mastering Bull Nose End Mill: Applications, Types, and Comparisons
Bull nose end mills are essential cutting tools in the world of machining, offering a unique blend of versatility and precision. As an experienced machinist or someone new to the field, understanding the intricacies of these tools can significantly enhance your projects’ quality and efficiency. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what a bull nose end mill is, its various applications, and how it compares to other popular cutting tools.
What is a Bull Nose End Mill?
A bull nose end mill, also known as a corner radius end mill, is a cutting tool used in milling operations. It features a rounded corner at the intersection of the end cutting edge and the side cutting edge. This rounded corner, or “bull nose,” gives the tool its name and distinctive appearance.

The bull nose design serves several crucial purposes:
- Increased tool strength: The rounded corner reduces stress concentration, making the tool less prone to chipping or breaking.
- Improved surface finish: The radius allows for smoother transitions between surfaces, resulting in a better overall finish.
- Enhanced chip evacuation: The rounded edge helps in efficient chip removal during cutting operations.
- Versatility: Bull nose end mills can perform both side and end milling operations, making them highly versatile tools.
When to Use a Bull Nose End Mill
Understanding when to use a bull nose end mill is crucial for optimizing your machining processes. Here are some common scenarios where these tools excel:
- Chamfering and Deburring: The rounded corner of a bull nose end mill makes it ideal for creating smooth, angled edges on workpieces. This is particularly useful in chamfering operations and for removing burrs left by previous machining processes.
- Contour Milling: When working on complex 3D shapes or contoured surfaces, bull nose end mills can provide smoother transitions between different planes, resulting in a more polished final product.
- Pocket Milling: The bull nose design allows for efficient material removal when creating pockets or cavities in a workpiece. The rounded corner helps reduce stress on the tool and workpiece during this process.
- Finishing Operations: Due to their ability to produce smooth surfaces, bull nose end mills are excellent choices for finishing passes, especially on contoured or sculptured surfaces.
- Shoulder Milling: When creating shoulders or steps in a workpiece, the bull nose end mill can provide a smoother transition at the corner, reducing stress concentration and improving the overall strength of the part.
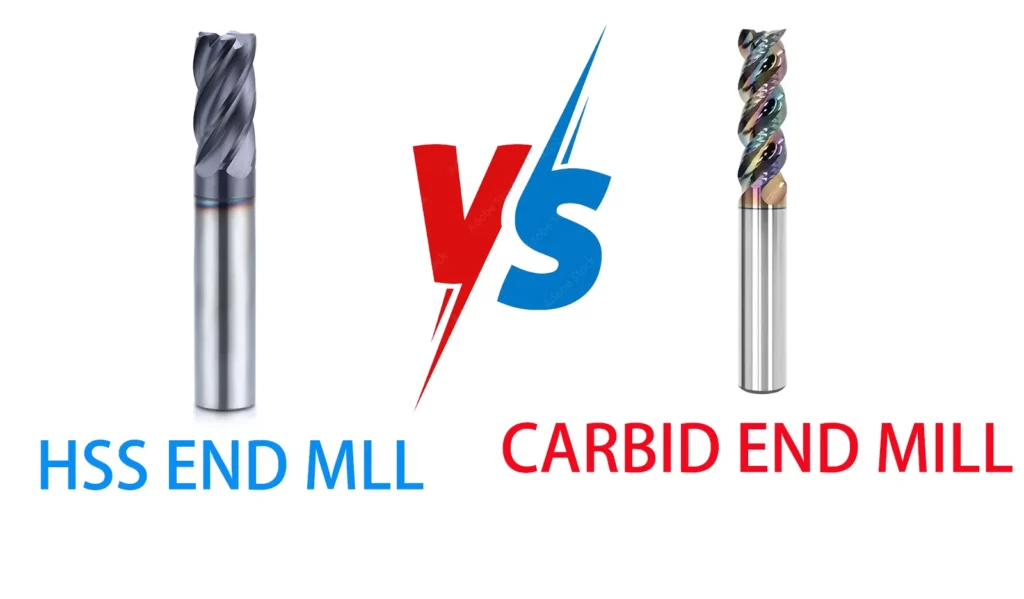
Bull Nose Carbide End Mill: A Cut Above the Rest
While bull nose end mills can be made from various materials, carbide bull nose end mills are particularly popular due to their superior performance characteristics. Here’s why:
- Hardness and Wear Resistance: Carbide is significantly harder than high-speed steel (HSS), allowing carbide bull nose end mills to maintain their cutting edge for longer periods, even when machining hard materials.
- Heat Resistance: Carbide tools can withstand higher temperatures without losing their hardness, making them suitable for high-speed machining operations.
- Rigidity: The stiffness of carbide allows for more precise cuts and better surface finishes, especially in applications requiring tight tolerances.
- Longevity: Due to their wear resistance, carbide bull nose end mills often have a longer tool life than their HSS counterparts, potentially reducing overall tooling costs in the long run.
- Productivity: The superior performance of carbide tools often allows for higher cutting speeds and feed rates, increasing overall productivity.
Bull Nose End Mill Radius: Choosing the Right Size
The radius of a bull nose end mill is a critical factor in its performance and application. Here are some considerations when selecting the appropriate radius:
- Smaller Radii (e.g., 0.005″ to 0.015″):
- Ideal for fine detail work and tight corners
- Provide sharper transitions between surfaces
- Useful in creating small fillets or chamfers
- Larger Radii (e.g., 0.030″ to 0.125″ or more):
- Offer increased tool strength
- Provide smoother surface finishes on larger parts
- Better suited for heavy material removal and roughing operations
- Intermediate Radii:
- Strike a balance between detail work and tool strength
- Versatile for a wide range of applications
When selecting the radius, consider factors such as the desired surface finish, the material being machined, and the specific requirements of your project.
Bull Nose End Mill Uses: Versatility in Action
The versatility of bull nose end mills makes them valuable in various industries and applications. Here are some common uses:
- Aerospace: Creating complex contoured surfaces on aircraft components
- Automotive: Machining engine blocks, cylinder heads, and transmission parts
- Mold Making: Producing smooth, contoured surfaces in mold cavities
- General Machining: Performing a wide range of milling operations, from roughing to finishing
- Medical Device Manufacturing: Creating precise, smooth surfaces on implants and surgical instruments
- Die and Tool Making: Producing dies and tools with smooth transitions and strong corners
Bull Nose End Mill vs Ball Nose: Understanding the Differences
While bull nose and ball nose end mills may seem similar at first glance, they have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. Let’s compare these two popular cutting tools:
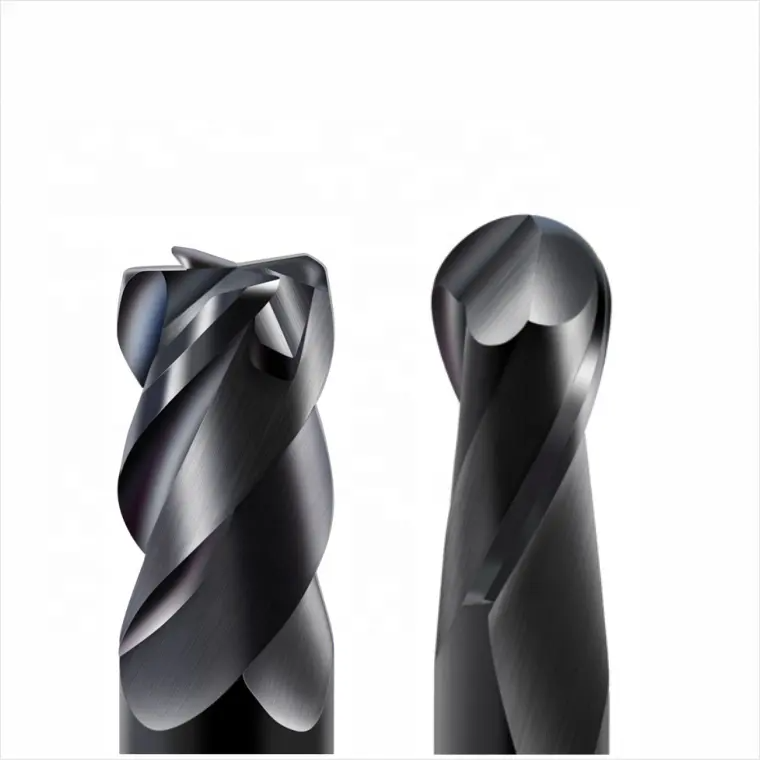

Bull Nose End Mill:
- Features a rounded corner at the intersection of the end and side cutting edges
- Maintains a flat bottom cutting surface
- Ideal for creating fillets, chamfers, and smooth transitions between surfaces
- Better suited for general-purpose milling and finishing operations
Ball Nose End Mill:
- Has a hemispherical (ball-shaped) end
- Excels at 3D contouring and sculpting operations
- Ideal for creating fully rounded corners and complex 3D shapes
- Often used in 3-axis and 5-axis machining centers for producing intricate parts
Bull Nose End Mill vs Flat End Mill: Choosing the Right Tool
Another common comparison is between bull nose and flat end mills. Understanding their differences can help you choose the most appropriate tool for your specific task:
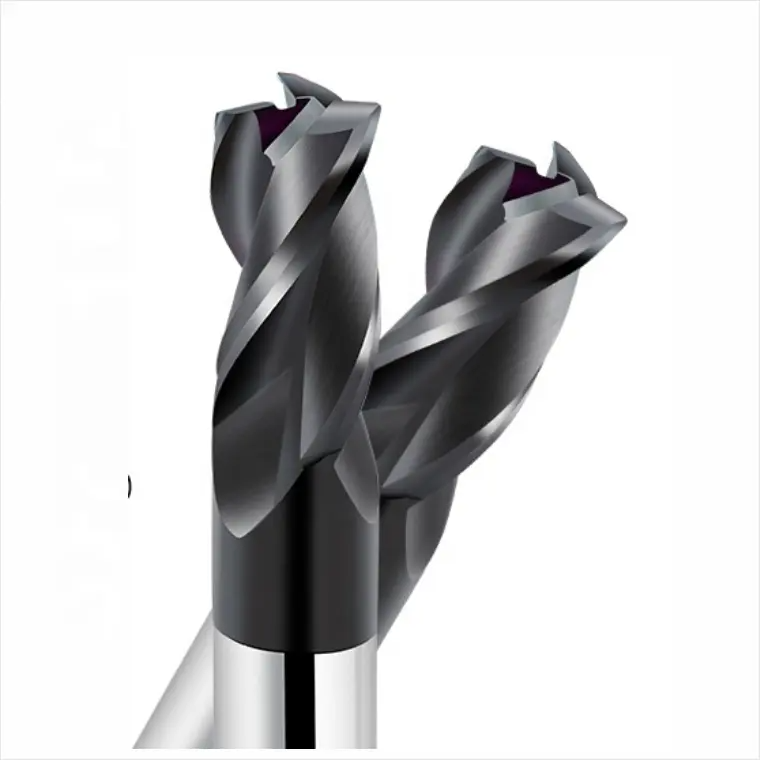

Bull Nose End Mill:
- Rounded corner provides increased tool strength
- Produces smoother transitions between surfaces
- Ideal for creating fillets and chamfers
- Better chip evacuation in some applications
- Can perform both side and end milling operations
Flat End Mill:
- Features sharp corners at the intersection of end and side cutting edges
- Produces crisp, 90-degree corners
- Ideal for creating flat-bottomed cavities and slots
- Generally more efficient for heavy material removal in flat surfaces
- May be more prone to chipping at the corners under heavy loads
Bull Nose vs. Flat End Mill: Application Considerations
When deciding between a bull nose and a flat end mill, consider the following factors:
- Surface Finish: If a smooth surface finish is crucial, especially at transitions between surfaces, a bull nose end mill is often the better choice.
- Corner Requirements: For applications requiring sharp, 90-degree corners, a flat end mill is more suitable.
- Tool Life: In applications with high stress on the tool corners, a bull nose end mill may offer longer tool life due to its increased strength.
- Material Removal Rate: For bulk material removal on flat surfaces, a flat end mill may be more efficient.
- Versatility: If you need a tool that can perform both side and end milling with smooth transitions, a bull nose end mill is often the more versatile option.
Difference Between Ball Nose and Bull Nose End Mill: A Closer Look
To further clarify the distinctions between ball nose and bull nose end mills, let’s examine their key differences:
- End Shape:
- Ball Nose: Fully hemispherical end
- Bull Nose: Flat end with rounded corners
- Cutting Action:
- Ball Nose: Point contact cutting, ideal for 3D contouring
- Bull Nose: Line contact cutting, better for general milling and finishing
- Surface Finish:
- Ball Nose: Produces a scalloped surface finish in 3D contouring
- Bull Nose: Creates smoother flat surfaces with rounded corners
- Application Focus:
- Ball Nose: Primarily used for 3D sculpting and contouring
- Bull Nose: More versatile, used for general milling, chamfering, and finishing
- Programming Considerations:
- Ball Nose: Often requires specialized CAM software for complex 3D paths
- Bull Nose: Generally simpler to program for most milling operations
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Bull Nose End Mills
Bull nose end mills are versatile and powerful tools in the world of machining. Their unique design, combining the benefits of flat and rounded cutting edges, makes them invaluable for a wide range of applications. From creating smooth transitions and fillets to performing general milling operations, bull nose end mills offer a balance of strength, precision, and versatility.
By understanding when to use a bull nose end mill, how it compares to other cutting tools like ball nose and flat end mills, and the importance of factors such as radius selection and material choice (e.g., carbide), machinists can optimize their processes and achieve superior results.
Whether you’re working in aerospace, automotive, mold making, or general machining, incorporating bull nose end mills into your toolset can enhance your capabilities and improve the quality of your finished products. As with any cutting tool, proper selection, use, and maintenance of bull nose end mills are key to maximizing their potential and ensuring the best possible outcomes in your machining projects.
What is a bull nose end mill?
A bull nose end mill is a specialized cutting tool used in milling operations. Here are the key points to understand about bull nose end mills:
Design: It features a rounded corner (the “bull nose”) at the intersection of the end cutting edge and the side cutting edge.
Purpose: The rounded corner serves to increase tool strength, improve surface finish, and enhance chip evacuation.
Structure: It has a flat bottom with rounded edges, combining elements of both flat and ball nose end mills.
Versatility: Bull nose end mills can perform both side and end milling operations.
Applications: They’re commonly used for chamfering, contouring, pocket milling, finishing operations, and creating smooth transitions between surfaces.
Benefits: The design reduces stress concentration, making the tool less prone to chipping or breaking, especially during heavy cutting operations.
Variations: Bull nose end mills come in various sizes and radii to suit different machining needs.
What is the difference between ball nose and end mills?
the primary difference between ball nose and end mills lies in their tip geometry, which directly impacts their suitability for different machining tasks. End mills excel at roughing and flat surfaces, while ball nose mills are preferred for finishing and intricate details
What is a bull nose radius?
A bull nose radius refers to a rounded edge or corner. It’s often used in various applications for aesthetic and functional purposes.
How do I know what end mill to use?
Choosing the right end milli requires a combination of factors such as workpiece material, machining method, type of end mill, number of flutes, diameter, coating and many other factors. For different machining needs, such as roughing, finishing, grooving, three-dimensional contouring, etc., you need to choose different types of end mill. For example, a larger diameter end mill with fewer flutes can be selected for roughing, while a smaller diameter end mill with more flutes can be selected for finishing.
Bull nose end mill sizes
While there’s a vast array of options, some common sizes for bull nose end mills include:
Diameter: 1/32″, 1/16″, 1/8″, 3/16″, 1/4″, 5/16″, 3/8″, 1/2 inch, and metric equivalents.
Corner Radius: Typically ranges from a small fraction of the diameter to a significant portion of it.
Shank Diameter: Common sizes include 1/8″, 3/16″, 1/4″, 5/16″, 3/8″, and 1/2 inch.