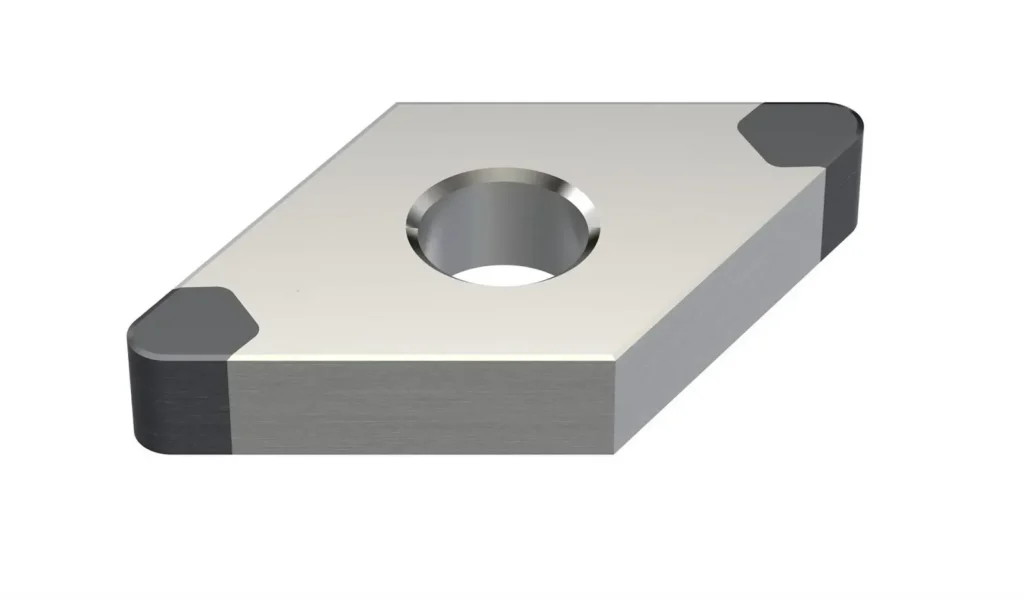
Comprehensive Guide to CBN Inserts: Composition, Applications, and Industry Usage
(Cubic Boron Nitride) CBN inserts are ultra-hard cutting tools used for machining high-hardness materials. This guide provides a detailed overview of CBN tools, their properties, applications, and industry-specific use cases.
Introduction to CBN Material
Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) is a remarkable synthetic material that has revolutionized the cutting tool industry. Discovered in 1957 by Robert H. Wentorf Jr. at General Electric, CBN is created by subjecting hexagonal boron nitride to extreme heat and pressure. This process transforms the soft, graphite-like structure of hexagonal boron nitride into a cubic crystal lattice, resulting in a material with extraordinary hardness and thermal stability. CBN’s unique properties stem from the strong covalent bonds between boron and nitrogen atoms in its cubic structure. While it’s the second hardest known material after diamond, CBN surpasses diamond in chemical stability and heat resistance, making it invaluable for machining ferrous materials and superalloys. The development of CBN has significantly advanced manufacturing capabilities, enabling the efficient processing of materials that were previously extremely challenging or impossible to machine effectively.
CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) tools are ultra-hard cutting tools used for machining high-hardness materials. This guide provides a detailed overview of CBN tools, their properties, applications, and industry-specific use cases.
Composition and Structure of CBN
CBN is a synthetic super-hard material, second only to diamond in hardness. It consists of nitrogen and boron atoms arranged in a cubic crystal structure, which gives it extremely high hardness and thermal stability. CBN inserts are typically made by sintering CBN particles under high temperature and pressure, then bonding them to a metal substrate.
Key Properties of CBN Inserts

- High Hardness: CBN’s hardness approaches that of diamond, enabling effective cutting of high-hardness materials like hardened steel, cast iron, and superalloys.
- Wear Resistance: Due to its high hardness and stable crystal structure, CBN tools exhibit excellent wear resistance, resulting in long tool life when machining high-hardness materials.
- Thermal Stability: CBN tools maintain stability at high temperatures, making them suitable for high-speed cutting and dry machining operations.
- Chemical Stability: CBN is chemically inert to ferrous metals, preventing chemical reactions with workpieces during the machining of iron-based materials.
- Thermal Conductivity: CBN has good thermal conductivity, which helps dissipate heat during cutting operations, reducing thermal damage to both the tool and the workpiece.
Applications of CBN Inserts
CBN tools are widely used in applications requiring high hardness and wear resistance:
- Hardened Steel: In automotive manufacturing and mold production, CBN tools are used for machining high-hardness steels after heat treatment.
- Cast Iron: Suitable for precision machining of gray cast iron and ductile iron.
- Powder Metallurgy Materials: Used for machining carbides and powder metallurgy parts.
- High-Temperature Alloys: In the aerospace industry, CBN tools are used for machining nickel-based and cobalt-based high-temperature alloys.
- Hardened Bearings: CBN tools are effective in machining hardened bearing components, improving efficiency and precision.
Types of CBN Inserts
CBN tools come in various types depending on their intended use and manufacturing process:
- CBN Turning Tools: Used for turning external diameters, internal bores, and face turning of high-hardness materials.
- CBN Milling Cutters: Used for milling flat surfaces and slots in hard materials.
- CBN Boring Tools: Used for precision boring operations.
- CBN Grinding Wheels: Used for high-precision grinding of hardened materials.
- CBN Inserts: Replaceable cutting edges that can be mounted on various tool holders for turning, milling, and boring operations.
Best Practices for Using CBN Inserts
- Optimize Cutting Parameters: Select appropriate cutting speed and feed rate based on the hardness and characteristics of the workpiece material to avoid excessive cutting temperatures and tool wear.
- Cooling and Lubrication: While CBN tools are suitable for dry cutting, using coolant in certain high-temperature machining operations can extend tool life.
- Rigid Clamping: Ensure rigid clamping of both the tool and workpiece to reduce vibration and improve machining stability and accuracy.
- Tool Path Strategy: Implement appropriate tool path strategies to maintain consistent cutting loads and minimize tool wear.
- Regular Tool Inspection: Periodically inspect CBN tools for wear and damage to maintain optimal cutting performance and workpiece quality.
Industry-Specific Applications of CBN Inserts
1. Automotive Manufacturing
Background: The automotive industry, particularly in engine and transmission part manufacturing, requires machining of high-hardness materials like hardened steel and cast iron.
Case Studies:
- Engine Block Machining: CBN tools are used to machine cylinder bores in engine blocks, improving efficiency and surface quality.
- Gear Production: In the hard turning of transmission gears, CBN tools significantly extend tool life and reduce machine downtime.
2. Aerospace Industry
Background: The aerospace industry extensively uses high-temperature alloys and titanium alloys, which are challenging to machine and demand high-performance tools.
Case Studies:
- Turbine Blade Machining: CBN tools are used to machine high-temperature alloy turbine blades, improving cutting efficiency and component accuracy.
- Structural Component Machining: CBN tools excel in machining titanium alloy structural components, reducing tool change frequency and increasing production efficiency.
3. Mold and Die Manufacturing
Background: Mold and die manufacturing involves machining large amounts of hardened alloys and high-hardness steels, requiring tools with high wear resistance and long life.
Case Studies:
- Injection Mold Machining: CBN tools are used for hard turning and grinding of injection molds, significantly improving machining precision and surface finish.
- Stamping Die Machining: In precision machining of stamping dies, the use of CBN tools extends die life and reduces maintenance costs.
4. Heavy Industry
Background: The mechanical processing industry needs to machine various high-hardness and difficult-to-machine materials, such as hardened steel and powder metallurgy materials.
Case Studies:
- Bearing Manufacturing: CBN tools are widely used in hard turning of bearing raceways, improving machining efficiency and bearing service life.
- Powder Metallurgy Part Machining: CBN tools perform excellently in machining powder metallurgy components, effectively reducing tool wear and improving production efficiency.
5. Energy Sector
Background: The energy sector involves machining many high-hardness and wear-resistant materials, such as components for oil drilling equipment and wind power generation equipment.
Case Studies:
- Oil Drilling Equipment: CBN tools are used to machine wear-resistant components of oil drilling equipment, significantly improving machining efficiency and component durability.
- Wind Power Generation Equipment: The use of CBN tools in machining gears and bearings for wind power generation equipment has improved component precision and lifespan.
6. Medical Device Manufacturing
Background: Medical device manufacturing requires high precision and surface quality, involving materials like titanium alloys and stainless steel that pose high demands on cutting tools.
Case Studies:
- Orthopedic Implant Machining: CBN tools are used to machine titanium alloy and stainless steel orthopedic implants, improving surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
- Dental Instrument Machining: In the precision machining of dental instruments, the use of CBN tools has significantly improved production efficiency and product quality.
Future Trends in CBN Insert Technology
- Nano-crystalline CBN: Development of CBN tools with nano-sized grains for improved hardness and wear resistance.
- Hybrid Tools: Combining CBN with other materials like ceramics or diamond to create tools with optimized properties for specific applications.
- Additive Manufacturing: Exploring the use of additive manufacturing techniques to produce CBN tools with complex geometries and optimized cooling channels.
- Smart Tools: Integration of sensors in CBN tools for real-time monitoring of tool wear and cutting conditions.
- Green Manufacturing: Development of CBN tools optimized for dry machining and minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) to reduce environmental impact.
These case studies and future trends demonstrate the wide-ranging applications and advantages of CBN tools across various industries. By judiciously selecting and utilizing CBN tools, manufacturers can significantly improve machining efficiency, workpiece quality, and tool life while reducing production costs.
What is a CBN insert?
A CBN insert is a cutting tool component made of Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN). It’s a small, replaceable piece that attaches to a larger tool holder. CBN inserts are designed to perform cutting operations on hard materials, typically those with a hardness of 45 HRC or higher.
What does “CBN inserts” mean?
“CBN inserts” refers to cutting tool inserts made from Cubic Boron Nitride. These inserts are used in various machining operations, particularly for hard turning, where they excel in cutting hardened steels, cast irons, and superalloys. The term encompasses the material (CBN) and the form factor (insert) of the cutting tool.
What are the applications of CBN inserts?
CBN inserts have a wide range of applications, primarily in hard machining operations:
Hard turning of bearing steels, tool steels, and case-hardened steels
Finishing operations on cast iron parts
Machining of powder metallurgy materials
Cutting of high-temperature alloys in aerospace applications
Precision machining of hardened gears and shafts in automotive manufacturing
Finishing operations in die and mold making
Who are the major CBN insert manufacturers?
Several leading cutting tool companies manufacture CBN inserts. Some of the prominent manufacturers include:
Sandvik Coromant
Kennametal
Mitsubishi Materials
Sumitomo Electric
Seco Tools
Iscar
Kyocera
ONMY Toolins
It’s important to note that the market is dynamic, and there may be other manufacturers or changes in the industry. Users should research current options and consult with suppliers to find the best fit for their specific needs.
What are typical speeds and feeds for CBN inserts?
Speeds and feeds for CBN inserts vary depending on the specific application, workpiece material, and insert grade. However, here are some general guidelines:
Cutting speed: For hardened steels (45-65 HRC): 100-250 m/min
For cast irons: 300-1500 m/min
For high-temperature alloys: 150-300 m/min
Feed rate: Roughing: 0.1-0.3 mm/rev
Finishing: 0.05-0.15 mm/rev
Depth of cut: Roughing: 0.2-2.0 mm
Finishing: 0.1-0.5 mm
These are general ranges, and actual parameters should be adjusted based on the specific insert grade, workpiece material properties, machine capabilities, and desired surface finish. Always consult the manufacturer’s recommendations and perform tests to optimize parameters for your specific application.
Remember that CBN inserts typically perform best at higher cutting speeds compared to conventional carbide tools. However, they also require more rigid machine setups and often benefit from specialized coolant strategies.