Indexable Inserts: The Cornerstone of Modern Machining
In the ever-evolving world of manufacturing and metalworking, precision and efficiency are paramount. Among the various tools that have revolutionized the industry, indexable inserts stand out as a game-changer. These small yet powerful components have transformed the way we approach cutting operations, offering unparalleled versatility and cost-effectiveness. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of indexable inserts, exploring their types, sizes, applications, and the tools that utilize them.
What is an Indexable Insert?
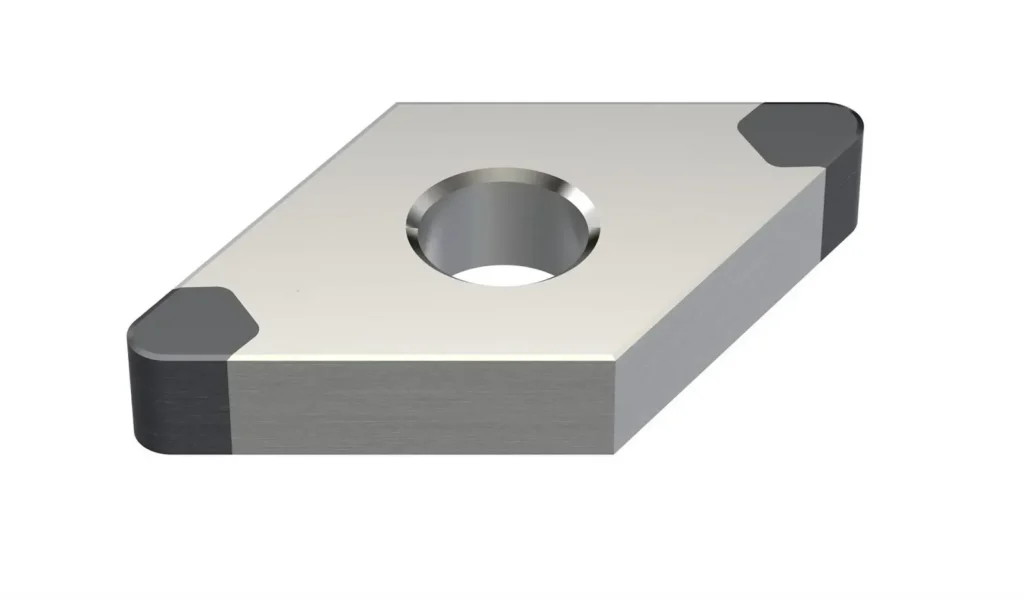
At its core, an indexable insert(Turning insert、Milling insert、U drill、Replaceble tip drill) is a removable cutting edge used in various machining operations. Unlike traditional solid cutting tools, indexable inserts are separate pieces that can be easily replaced or rotated when one cutting edge becomes dull. This innovative design allows for multiple cutting edges on a single insert, significantly extending the tool’s life and reducing downtime.
Indexable inserts are typically made from advanced materials such as carbide, ceramic, or polycrystalline diamond (PCD), each offering specific advantages depending on the application. These inserts are designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them ideal for a wide range of cutting operations, from roughing to finishing.

The Evolution of Indexable Inserts
The concept of indexable cutting tools dates back to the early 20th century, but it wasn’t until the 1950s that they gained widespread adoption in the manufacturing industry. As materials science and production techniques advanced, so did the quality and variety of indexable inserts. Today, they are an indispensable part of modern machining, offering benefits such as:
- Increased productivity
- Reduced tool changes
- Improved surface finish
- Enhanced cutting speeds and feeds
- Lower overall tooling costs
Indexable Insert Types
The world of indexable inserts is vast and varied, with different types designed to meet specific machining requirements. Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the right insert for your application. Here are some of the most common indexable insert types:
- Turning Inserts Turning inserts are used in lathe operations and come in various shapes, including diamond, triangle, square, and round. Each shape offers different cutting characteristics and is suited for specific turning applications.
- Milling Inserts Milling inserts are designed for use in milling cutters and end mills. They come in a variety of geometries, such as square, round, and octagonal, each optimized for different milling operations.
- Drilling Inserts These inserts are specifically designed for drilling operations and are often used in conjunction with indexable drill bodies. They offer improved performance and longevity compared to traditional twist drills.
- Threading Inserts Threading inserts are used to create both internal and external threads. They come in various profiles to match different thread standards and pitches.
- Grooving and Parting Inserts These specialized inserts are used for creating grooves or separating workpieces in turning operations. They typically have a narrow profile to minimize material waste.
Indexable Insert Sizes
Indexable insert sizes play a crucial role in determining the appropriate tooling for a specific machining operation. The size of an insert affects factors such as cutting depth, feed rate, and overall tool performance. Insert sizes are typically specified using a standardized naming convention that includes:(Check out our other articles for specific naming rules)
- Insert Shape: Denoted by a letter (e.g., C for 80° diamond, S for square 90°)
- Relief Angle: Indicated by a letter (e.g., Turning insert and milling insert C for 7°, N for 0°;)
- Tolerance Class: Represented by a letter (e.g., M for IC±0.05-±0.15)
- Size Code: A two-digit number representing the insert’s inscribed circle diameter or cutting edge length(Such as round insert 06 represented 6mm))
For example, an insert designated as CNMG 120408 would be an 80° diamond shape (C) with a 0° relief angle (N), medium tolerance (M), and a size code of 120408(12.7mm internally connected circle,4.76mm insert thickness and 0.8mm insert tip radius).
Understanding these size designations is crucial for selecting the right insert for your specific machining needs and ensuring compatibility with your toolholders.
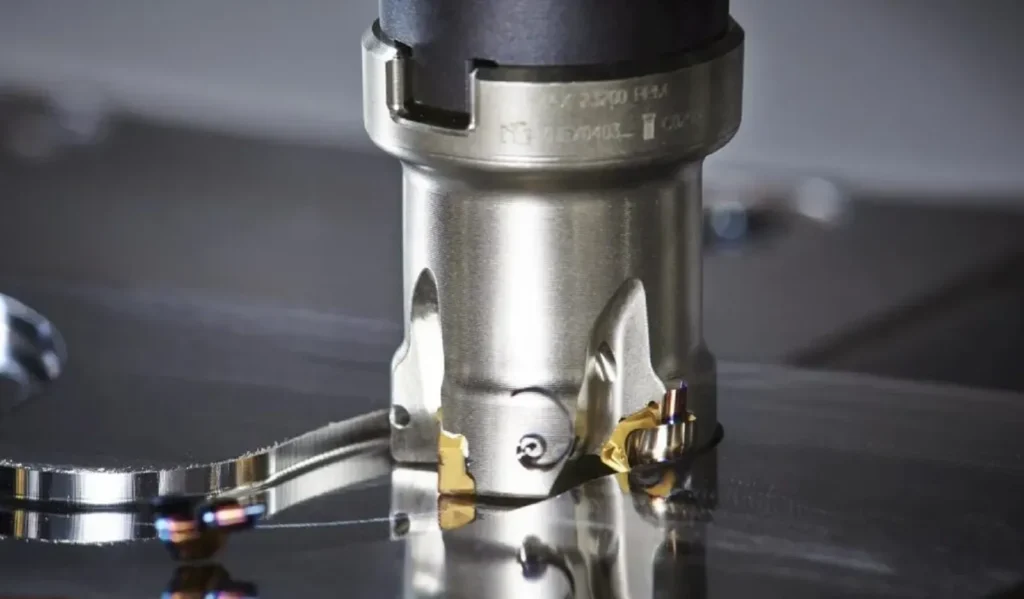
What is an Indexable End Mill Used For?

Indexable end mills are milling tools that can be used for a variety of applications, including roughing, side milling, contouring, and helical interpolations. They are well-suited for efficient production runs because of their large diameter and high feed rate capacity. They can also be used for applications that require shallow depths of cut (0.100″ or less).
An indexable end mill is a versatile cutting tool that combines the benefits of traditional solid end mills with the advantages of indexable inserts. These tools are primarily used in milling operations and offer several key advantages:
- Cost-effectiveness: While the initial cost might be higher, indexable inserts are more economical in the long run. When one cutting edge dulls, you can simply rotate or replace the insert rather than replacing an entire tool.
- Reduced downtime: Changing or rotating an insert is much quicker than replacing or regrinding a solid tool, significantly reducing machine downtime.
- Consistent performance: Each new cutting edge provides consistent, like-new performance, ensuring uniform quality across production runs.
- Versatility: A single tool holder can accommodate different insert grades and geometries, allowing for quick adaptations to various materials and cutting conditions.
- Improved tool life: The ability to use multiple cutting edges on a single insert extends the overall life of the tooling system.
- Higher cutting speeds: Many indexable inserts are made from advanced materials that can withstand higher cutting speeds than traditional tools.
- Precision and repeatability: Indexable inserts are manufactured to tight tolerances, ensuring consistent dimensions and cutting performance.
- Inventory management: Stocking a variety of inserts takes up less space and is easier to manage than maintaining an inventory of solid cutting tools.
- Material optimization: Indexable inserts allow for the use of premium cutting materials (like carbide or ceramics) only where needed, reducing overall material costs.
- Sustainability: The ability to replace only the cutting edge rather than the entire tool contributes to reduced waste and more sustainable machining practices.
Typical applications for indexable end mills include:

- Heavy-duty roughing operations
- High-speed milling of large surfaces
- Machining of difficult-to-cut materials
- Complex profiling and contouring
- Shoulder milling and slot milling
The versatility and efficiency of indexable end mills make them a popular choice in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and general manufacturing.
What is an Indexable Tool Holder?
An indexable tool holder is a crucial component in the machining process, designed to securely hold and position indexable inserts during cutting operations. These tool holders come in various designs to accommodate different insert shapes, sizes, and machining applications. The primary functions of an indexable tool holder include:
- Insert Retention: Securely holding the insert in place during high-speed and high-force cutting operations.
- Precision Positioning: Ensuring the insert is positioned at the correct cutting angle and depth for optimal performance.
- Coolant Delivery: Many indexable tool holders feature internal coolant channels to direct cutting fluid precisely to the cutting edge.
- Vibration Dampening: Some advanced tool holders incorporate features to reduce vibration, improving surface finish and tool life.
- Quick Change Capability: Facilitating rapid insert changes to minimize machine downtime.
Types of Indexable Tool Holders
- Turning Tool Holders: Used in lathe operations for external and internal turning, facing, and grooving.
- Milling Cutter Bodies: Designed to hold multiple inserts for face milling, shoulder milling, and other milling operations.
- Boring Bars: Used for internal machining operations, particularly in deep-hole boring.
- Indexable Drill Bodies: Specifically designed to hold drilling inserts for high-performance hole-making operations.
- Threading Tool Holders: Engineered to hold threading inserts at the correct angle for precise thread cutting.
Selecting the right indexable tool holder is crucial for maximizing the performance of your indexable inserts and achieving optimal machining results.
Maximizing Efficiency with Indexable Inserts
To fully leverage the benefits of indexable inserts in your machining operations, consider the following best practices:
- Proper Insert Selection: Choose the right insert grade, geometry, and size for your specific material and cutting conditions.
- Correct Tool Holder Pairing: Ensure your indexable tool holder is compatible with the chosen insert and provides the necessary stability and precision.
- Optimal Cutting Parameters: Use recommended cutting speeds, feed rates, and depths of cut to maximize insert life and performance.
- Regular Maintenance: Inspect inserts and tool holders regularly for wear or damage, and replace or rotate inserts as needed.
- Coolant Management: Utilize appropriate coolant strategies to enhance chip evacuation and extend insert life.
- Continuous Improvement: Stay informed about new insert technologies and grades to continuously optimize your machining processes.
Conclusion
Indexable inserts have revolutionized the world of machining, offering unparalleled flexibility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. By understanding the various types of indexable inserts, their sizes, and the tools that utilize them, manufacturers can significantly enhance their cutting operations. Whether you’re performing high-speed milling with an indexable end mill or precision turning with a specialized insert, the right combination of insert and tool holder can dramatically improve your machining outcomes.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see further innovations in indexable insert design and materials, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in metal cutting. By staying informed and embracing these advancements, manufacturers can maintain a competitive edge in an increasingly demanding industry.
What is the difference between indexable end mill and face mill?
Indexable end mills and face mills differ primarily in their design and application. End mills are cylindrical tools that can cut both axially and radially, making them versatile for operations like profiling, slotting, and contouring. They’re typically smaller in diameter and can perform deeper cuts relative to their size. Face mills, on the other hand, are disc-shaped tools designed primarily for surface milling large, flat areas. They have inserts mounted on their face and cut perpendicular to the tool axis, allowing for wider cuts and higher material removal rates on flat surfaces. While end mills offer more versatility and precision for complex geometries, face mills excel at quickly achieving flat, even surfaces over large areas.
What are the advantages of indexable inserts?
Indexable inserts offer numerous advantages in machining operations, making them a popular choice in modern manufacturing. They provide cost-effectiveness through their ability to be rotated or replaced when one cutting edge dulls, significantly reducing downtime compared to replacing entire tools. These inserts deliver consistent performance with each new cutting edge, ensuring uniform quality across production runs. Their versatility allows a single tool holder to accommodate various insert grades and geometries, adapting to different materials and cutting conditions. Indexable inserts can withstand higher cutting speeds, improve overall tool life, and offer precision due to tight manufacturing tolerances. They also contribute to better inventory management and sustainability by reducing waste. These benefits combine to enhance productivity, flexibility, and efficiency in machining processes across various industries.
What does “indexable” mean in machining?
In machining, “indexable” refers to a cutting tool design that features replaceable and rotatable cutting edges, typically in the form of small, precisely shaped inserts. This term signifies that the cutting edges can be “indexed,” or rotated to a new position, when one edge becomes worn. Indexable tools allow operators to quickly change or reposition the cutting edge without replacing the entire tool body. This design offers several advantages, including extended tool life, reduced downtime for tool changes, consistent cutting performance, and cost-effectiveness. The ability to index also means that a single tool can often accommodate different insert shapes or grades, providing versatility for various machining operations and materials. This indexable concept has revolutionized modern machining by improving efficiency, reducing tooling costs, and enhancing overall productivity in metalworking processes.
What is an indexable end mill?
An indexable end mill is a versatile cutting tool used in milling operations that combines the functionality of traditional solid end mills with the advantages of replaceable cutting inserts. It consists of a cylindrical tool body with multiple pockets or seats designed to hold small, precisely shaped cutting inserts. These inserts can be easily rotated or replaced when worn, allowing for quick edge changes without replacing the entire tool. Indexable end mills can perform various milling operations, including face milling, side milling, slotting, and profiling. They offer benefits such as reduced tooling costs, consistent cutting performance, and the flexibility to use different insert grades or geometries on the same tool body. This design makes indexable end mills particularly effective for heavy-duty machining, working with difficult materials, and applications requiring high material removal rates while maintaining efficiency and precision.
What is unique about indexable insert drills?
Indexable insert drills are unique cutting tools that offer several distinct advantages in drilling operations. Unlike traditional solid drills, these tools feature a drill body with replaceable cutting inserts, typically positioned at the tip and outer edges. This design allows for quick and easy replacement of worn cutting edges without changing the entire drill, significantly reducing downtime and tooling costs. Indexable insert drills often provide superior chip evacuation through specially designed flutes and internal coolant channels, enhancing performance in deep-hole drilling. They offer versatility by allowing the use of different insert grades and geometries to optimize cutting for various materials and conditions. These drills generally achieve higher cutting speeds and feed rates compared to conventional drills, resulting in improved productivity. Additionally, the ability to fine-tune the position of the inserts enables precise control over hole diameter and straightness, making indexable insert drills particularly valuable for high-precision applications in industries such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing.