The Ultimate Guide to CNC Inserts: Types, Materials, and Applications
Introduction:
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, offering precision, efficiency, and versatility in producing complex parts. At the heart of this technology lies a crucial component: the CNC insert. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about CNC inserts, from their types and materials to their applications in various industries.\
What are CNC Inserts?

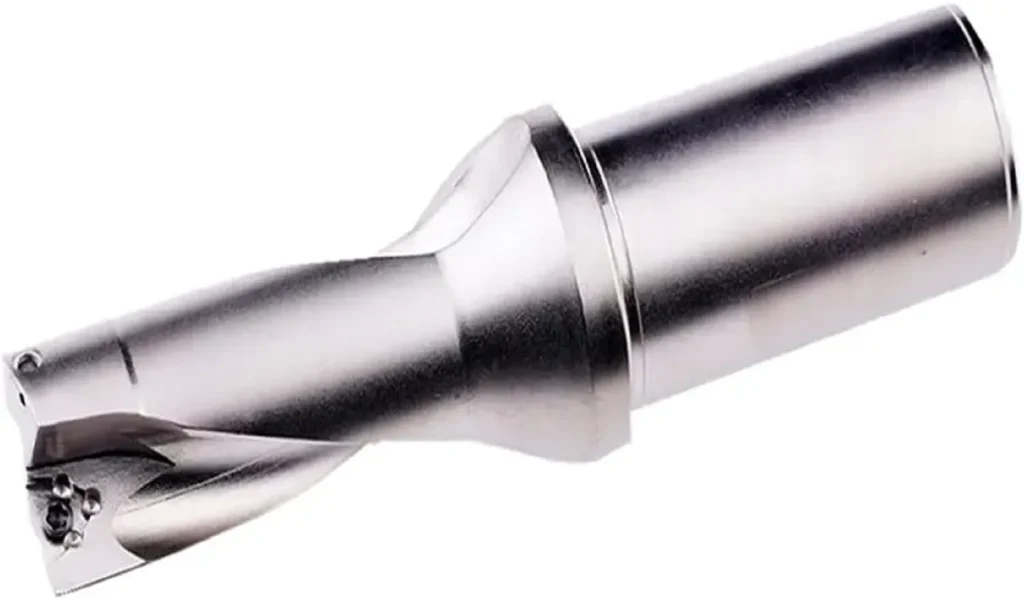
CNC inserts are small, replaceable cutting tools used in CNC machines to remove material from workpieces. These inserts are designed to be easily interchangeable, allowing operators to quickly replace worn or damaged cutting edges without changing the entire tool holder. This system enhances efficiency, reduces downtime, and provides cost-effective machining solutions.
CNC Insert Nomenclature:
Understanding CNC insert nomenclature is essential for selecting the right tool for your machining needs. The naming convention follows a standardized system that provides information about the insert’s shape, size, thickness, and other characteristics. Let’s break down the key components of CNC insert nomenclature:
- Shape: The first letter indicates the insert’s shape (e.g., C for 80° diamond, S for square, T for triangle).
- Relief angle: The second letter represents the insert’s relief angle.
- Tolerance class: The third letter denotes the insert’s dimensional tolerance.
- Insert features: Additional letters may indicate special features like chip breakers or wiper geometry.
- Size: A two-digit number represents the inscribed circle diameter or cutting edge length.
- Thickness: Another two-digit number indicates the insert’s thickness.
- Corner radius: The final letter and number combination specifies the corner radius.
Understanding this nomenclature is crucial when selecting inserts from a CNC insert chart or catalog, ensuring you choose the right tool for your specific application.
Types of CNC Inserts:
There are various CNC insert types available, each designed for specific machining operations and materials. Some common types include:
- Turning inserts: Used for cylindrical turning operations.
- Milling inserts: Designed for face milling, shoulder milling, and other milling applications.
- Threading inserts: Specialized for creating external and internal threads.
- Grooving and parting inserts: Used for creating grooves or separating workpieces.
- Boring inserts: Designed for enlarging and finishing holes.
- Drilling inserts: Used in indexable drill bodies for hole-making operations.
Each type of insert is available in various shapes, sizes, and geometries to suit different machining requirements and workpiece materials.
CNC Insert Materials:
The choice of CNC insert material significantly impacts machining performance, tool life, and surface finish. Common CNC insert materials include:
- Carbide: The most widely used insert material, offering excellent hardness and wear resistance.
- Cermet: A composite material combining ceramic and metallic elements, providing good wear resistance and toughness.
- Ceramic: Ideal for high-speed machining of hard materials, offering excellent heat resistance.
- Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN): Used for machining hardened steels and cast irons.
- Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD): Suitable for machining non-ferrous metals and abrasive materials.
Selecting the appropriate insert material depends on factors such as workpiece material, cutting conditions, and desired surface finish.
Applications of CNC Inserts:

CNC inserts find applications across various industries and machining operations:
- Metal CNC Insert Applications:
- Automotive: Engine components, transmission parts, brake rotors
- Aerospace: Turbine blades, structural components, landing gear parts
- Oil and Gas: Valve bodies, pump components, drilling equipment
- General Engineering: Shafts, gears, bearings, and other precision parts
- Wood CNC Insert Applications: While less common than metal machining, wood CNC inserts are used in:
- Furniture manufacturing: Creating intricate designs and joinery
- Woodworking: Producing custom moldings, carvings, and decorative elements
- Musical instrument making: Crafting guitar bodies, necks, and other components
Choosing the Right CNC Insert:
Selecting the appropriate CNC insert involves considering several factors:
- Workpiece material: Match the insert grade to the material being machined.
- Cutting parameters: Consider speed, feed, and depth of cut requirements.
- Machine stability: Choose inserts that can handle the rigidity of your machine setup.
- Surface finish requirements: Select inserts with appropriate edge preparation and coatings.
- Tool life expectations: Balance performance with tool life based on production needs.
Many manufacturers offer CNC insert kits that provide a range of insert options for different applications, allowing users to experiment and find the best solution for their specific needs.
Optimizing CNC Insert Performance:
To maximize the performance and longevity of your CNC inserts:
- Ensure proper insert seating and clamping in the tool holder.
- Use appropriate cutting parameters as recommended by the insert manufacturer.
- Implement effective chip control strategies to prevent chip buildup and damage.
- Monitor insert wear and replace inserts before they fail to maintain part quality.
- Use high-quality coolants and lubrication to reduce heat and friction during machining.
Conclusion:
CNC inserts play a crucial role in modern manufacturing, offering versatility, efficiency, and precision in machining operations. By understanding CNC insert nomenclature, types, materials, and applications, machinists and engineers can make informed decisions to optimize their machining processes. Whether you’re working with metal or wood, selecting the right CNC insert is key to achieving high-quality results and maximizing productivity in your CNC machining operations.
Remember to consult CNC insert charts and manufacturer recommendations when selecting inserts for your specific applications. With the right knowledge and tools, you can harness the full potential of CNC inserts to elevate your machining capabilities and achieve superior results in your manufacturing processes.
What is a CNC insert?
A CNC insert is a replaceable cutting tool used in CNC machining operations to remove material from workpieces.
How do I read a CNC insert code?
CNC insert codes follow a standardized nomenclature that indicates shape, relief angle, tolerance, size, thickness, and corner radius. Each part of the code represents specific characteristics of the insert.
What are the most common CNC insert shapes?
Common shapes include square, triangular, diamond, round, and hexagonal inserts.
How often should I replace my CNC inserts?
Replacement frequency depends on factors like material being cut, cutting parameters, and insert quality. Monitor insert wear and replace when cutting performance deteriorates.
Can I sharpen CNC inserts?
Most CNC inserts are designed to be disposable and are not meant to be resharpened. However, some specialized inserts can be reground.
What’s the difference between positive and negative rake inserts?
Positive rake inserts have a lifting angle on the top surface, reducing cutting forces but with less strength. Negative rake inserts are stronger but require more cutting force.
How do I choose the right insert grade?
Select the insert grade based on the workpiece material, cutting conditions, and desired balance between wear resistance and toughness.
What causes insert chipping?
Chipping can be caused by excessive feed rates, improper insert seating, or machining interruptions.
Are CNC inserts universal?
No, CNC inserts are not universal. They are designed for specific tool holders and cutting applications.
How do I improve insert tool life?
Improve tool life by using appropriate cutting parameters, ensuring proper insert seating, using coolant, and selecting the right insert for your application.
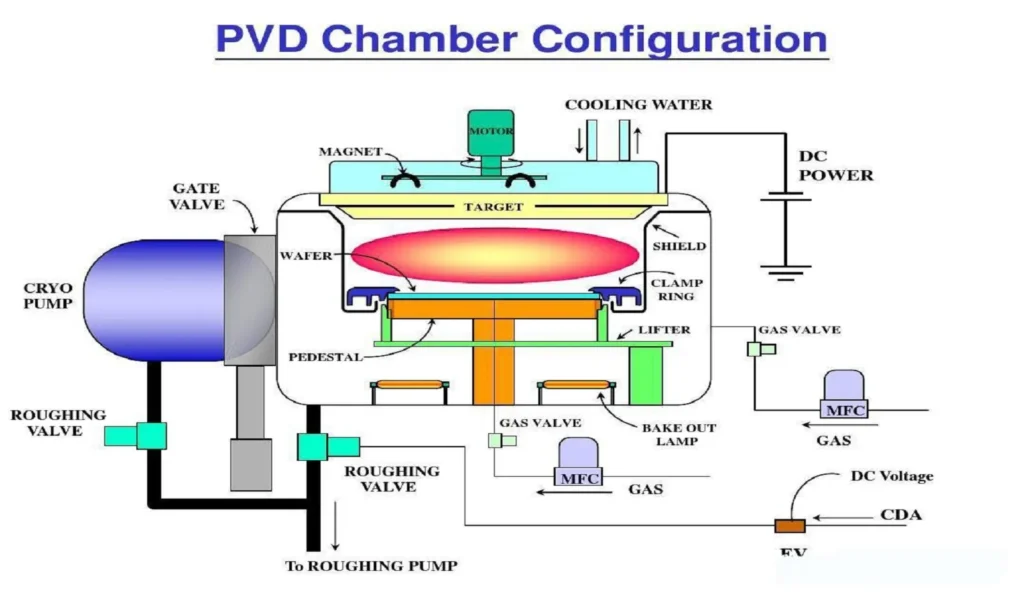


Great read! CNC machining is truly a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. The precision, efficiency, and repeatability it offers are unmatched, especially for complex parts and tight tolerances. I also appreciate how it reduces human error and speeds up production time without compromising quality. It’s amazing to see how CNC technology continues to evolve, making it even more accessible for both large industries and small workshops. Thanks for sharing such informative content!