Milling is essentially an intermittent machining process. This would cause the temperature at the cutting edge to fluctuate continuously between high temperatures (around 1000 °C) and low temperatures. What follows is which is better wet milling or dry milling (wet milling vs dry milling).
Effects of Cutting Fluids
When the cutting edge enters and exits cutting, the temperature fluctuation is exacerbated. Therefore, the cutting edge undergoes thermal shocks and cyclic stresses, which can result in cracking and prematurely ending the effective tool’s life in the worst cases.
The higher the temperature at the cutting zone, the less suitable it is to use cutting fluids.
In fine machining processes, since less heat is generated, using cutting fluids will not significantly shorten tool life as in roughing.
Dry Milling
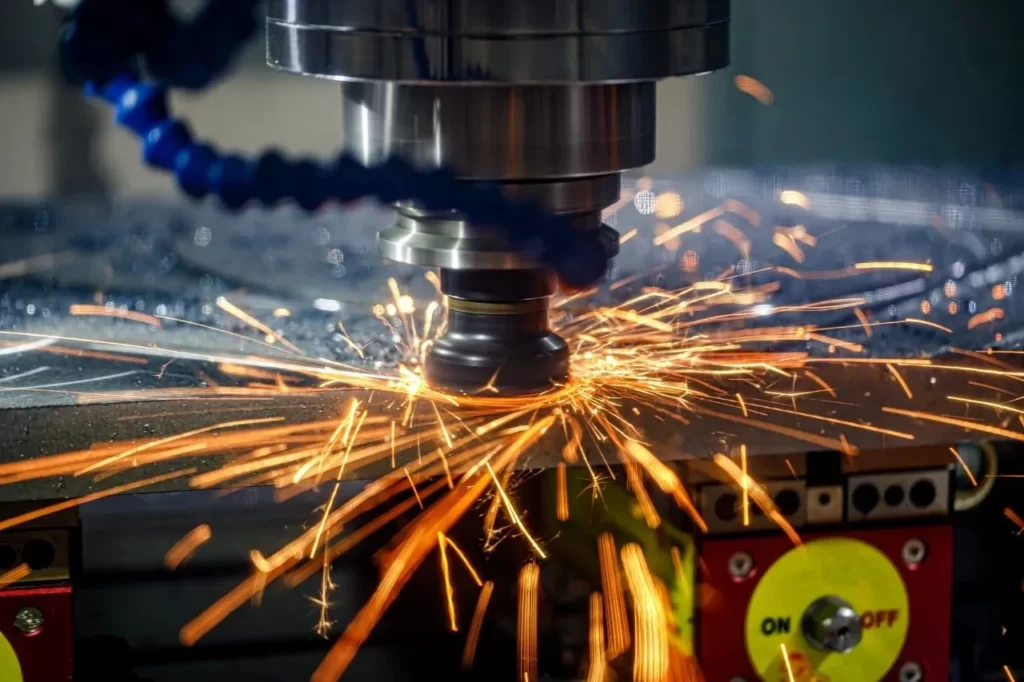

Dry milling can prolong the tool life of the cutting edge. While temperatures will still fluctuate, they will remain within the design range of the hard metal alloy material. Rough milling operations should always be performed without the use of cutting fluids.
Wet Milling with the Use of Cutting Fluids
There are some exceptions where cutting fluids should be used:
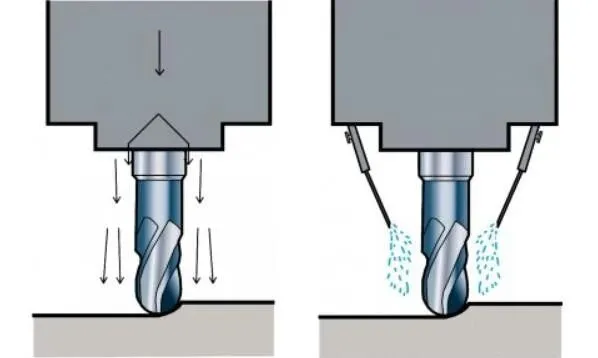
(1) Finishing of stainless steels and aluminum alloys to prevent metal particles from embedding in surface textures.
(2) Milling of high-temperature alloys at low cutting speeds for lubrication and cooling of the workpiece.
(3) Milling of cast iron to wet and flush away dust for environmental/health protection and accuracy of parts.
(4) Milling of thin-walled parts to prevent geometric deformation.

(5) When machining deep cavities, minimal quantity lubrication systems (MQL) using small amounts of dedicated oil with compressed air can assist with chip removal.
In MQL systems, the “oil mist” quantity is only a few milliliters of oil per hour expelled through a conventional filtered ventilation system.
If wet milling must be performed, sufficient quantities of cutting fluid should be used.
What are the main differences between the two milling methods?
Wet milling uses cutting fluid, while dry milling does not use cutting fluid.
What are the advantages of using cutting fluid?
Using cutting fluid can cool the temperature at the cutting zone, reduce thermal shock, and prolong tool life. Meanwhile, cutting fluid can also remove the swarf and protect the environment.
What are the advantages of dry milling?
Dry milling does not require the use and processing of cutting fluid, so the operating cost is lower. In addition, dry milling makes temperature fluctuations smaller, which benefits the tool.
In which situations are the two methods applicable?
Wet milling is suitable for the machining of high-temperature alloys that require cooling. Dry milling is suitable for rough machining and situations with low environmental pollution requirements.
How to select a suitable milling method?
Material properties, machining depth, accuracy requirements, etc. should be considered to choose the optimal method, balancing cost and efficiency. MQL methods may also be used for some special materials.
conclusion
Both methods have their pros and cons. A flexible approach to choosing the most appropriate method based on the specific application is recommended to achieve quality results efficiently. Proper technique is also important for maximizing tool life and performance.
In summary, selecting wet or dry milling depends on the technical and economic evaluation of each individual machining situation. An integrated approach weighing different factors leads to the best outcome.