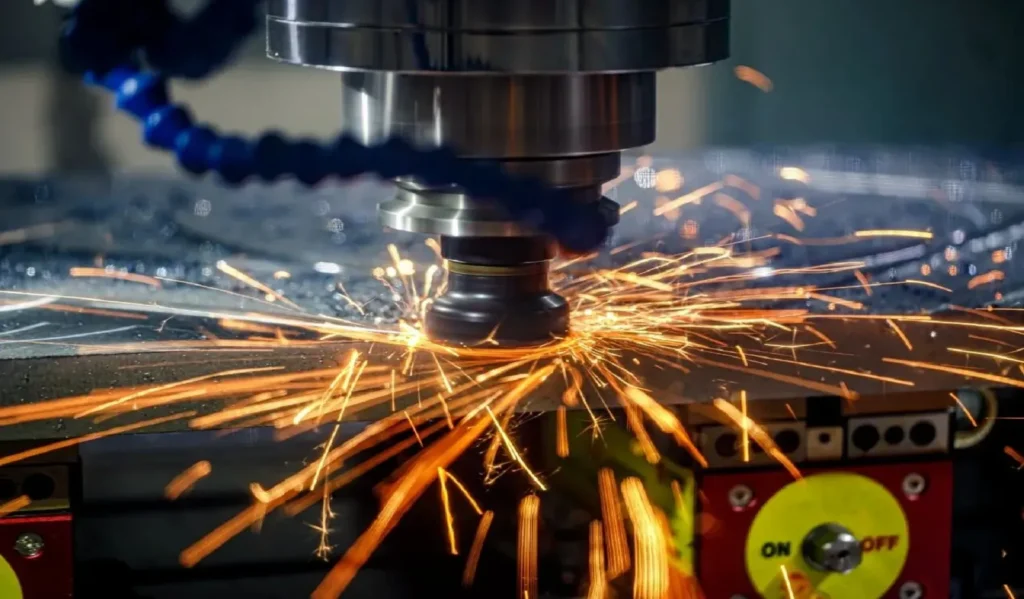
Dans le monde de l'usinage de précision, disposer des bons outils peut faire toute la différence entre un bon et un excellent produit. Parmi ces outils essentiels, le foret en U s'impose comme une option polyvalente et efficace pour créer des trous de haute qualité dans divers matériaux. Ce guide complet se penche sur l'univers des forets en U, en explorant leurs caractéristiques, leurs applications et les meilleures pratiques d'utilisation.
Qu'est-ce qu'un exercice en U ?
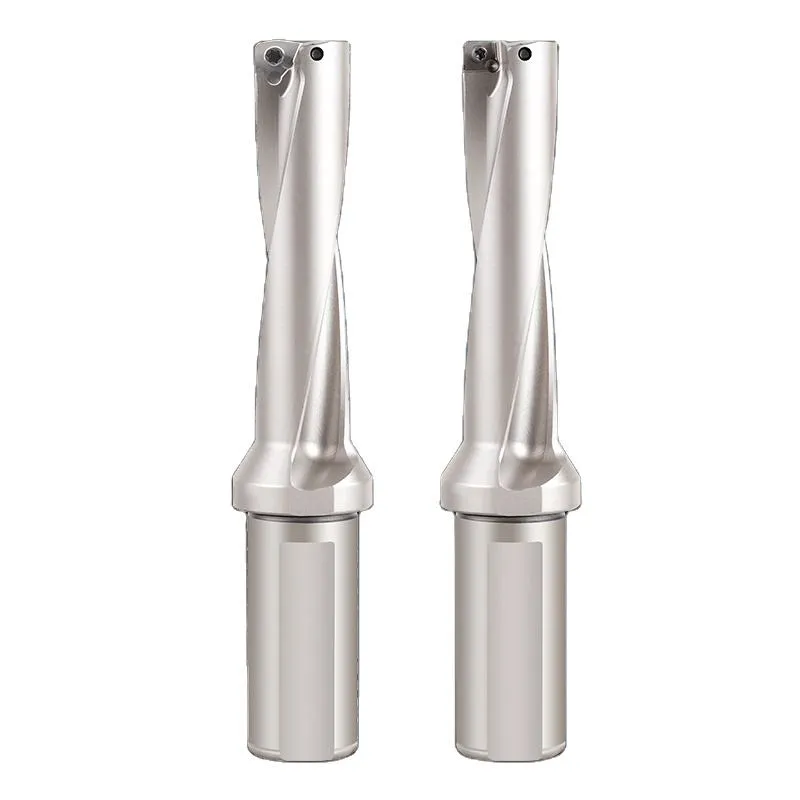

A Foret U, également connu sous le nom de foret à plaquettes indexables, est un outil de coupe spécialisé conçu pour réaliser des perçages efficaces et précis. Contrairement aux forets hélicoïdaux traditionnels, Exercices en U présentent une conception unique en forme de U qui permet une meilleure évacuation des copeaux et améliore les performances de coupe. Cette conception innovante rend les forets en U particulièrement adaptés à l'usinage à grande vitesse et aux applications nécessitant une qualité de trou supérieure.
Les principales caractéristiques des foreuses U sont les suivantes
- Plaquettes en carbure remplaçables
- Capacités d'autocentrage
- Excellent contrôle des puces
- Vitesses de coupe et vitesses d'avance élevées
- Polyvalence pour différents matériaux
Tableau des tailles de forets en U et tailles standard
Comprendre Foret U Les dimensions sont cruciales pour choisir l'outil adapté à votre application spécifique. Foret U Les tableaux des dimensions comprennent généralement des informations sur le diamètre de perçage, la longueur totale et les spécifications des inserts. Les dimensions standard des forets en U vont de petits diamètres de 0,472 pouce (12 mm) à des dimensions plus importantes de 2,559 pouces (65 mm) ou plus, selon le fabricant.
Lors de la consultation d'un Tableau des tailles de forets en U, Pour ce faire, il faut tenir compte des facteurs suivants :
- Diamètre de trou requis
- Matériau foré
- Profondeur du trou
- Spécifications de la machine
Il est important de noter que les tailles des forets en U peuvent varier légèrement d'un fabricant à l'autre. Il convient donc de toujours se référer au tableau des tailles des forets en U fourni par votre fournisseur d'outillage.
Applications du foret en U
Les forets en U trouvent des applications dans un large éventail d'industries et de matériaux en raison de leur polyvalence et de leur efficacité. Parmi les applications courantes des forets en U, on peut citer
- Automobile : Blocs moteurs, boîtiers de transmission, composants de freinage
- Aérospatiale : Composants structurels, pièces de trains d'atterrissage
- Pétrole et gaz : Trépans, vannes, brides
- Fabrication générale : Cadres de machines, moules, matrices
Les forets U permettent de percer divers matériaux, notamment :
- Acier et acier inoxydable
- Fonte
- Aluminium et autres métaux non ferreux
- Composites
Techniques d'utilisation des forets en U sur les machines-outils à commande numérique
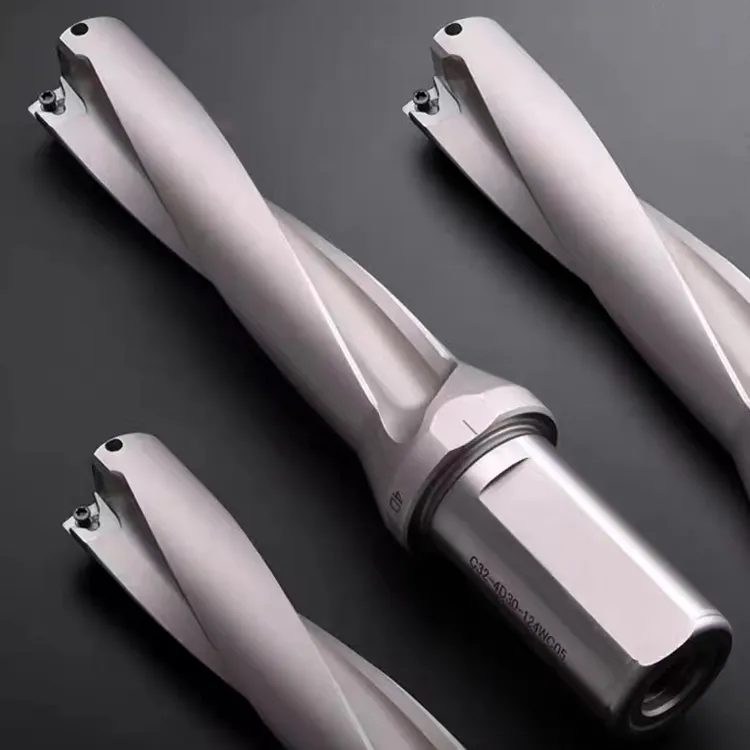

- Exercices en U nécessitent une grande rigidité de la machine-outil et un centrage outil-pièce, et conviennent donc à une utilisation sur des machines-outils CNC de grande puissance, de grande rigidité et à grande vitesse.
- Lorsque vous utilisez des forets en U, choisissez des plaquettes ayant une bonne ténacité pour la plaquette centrale et des plaquettes plus tranchantes pour les plaquettes périphériques.
- Pour différents matériaux, sélectionnez des plaquettes avec différentes formes de fentes pour les copeaux. En général, pour les petites avances, les petites tolérances et les rapports alésage/diamètre plus importants, il convient d'utiliser des plaquettes avec des forces de coupe plus faibles, alors que pour l'ébauche, les grandes tolérances et les rapports alésage/diamètre plus faibles, il convient d'utiliser des plaquettes avec des forces de coupe plus importantes.
- Tenez toujours compte de la puissance de la broche de la machine, de la stabilité du serrage du foret U, de la pression et du débit du liquide de refroidissement pendant l'utilisation, et contrôlez l'enlèvement des copeaux pour éviter d'affecter la rugosité de la surface du trou et la précision dimensionnelle.
- Assurez-vous que le centre du foret en U coïncide avec la surface de la pièce et qu'il est perpendiculaire à celle-ci pendant le serrage.
- Sélectionner les paramètres de coupe appropriés en fonction du matériau de la pièce.
- Pendant la coupe d'essai, ne réduisez pas imprudemment les vitesses d'avance ou les vitesses de rotation afin d'éviter de casser ou d'endommager la Insert de foret U ou outil.
- Lorsque les plaquettes s'usent ou se cassent en cours d'utilisation, il convient d'en analyser soigneusement les raisons et de les remplacer par des plaquettes plus robustes ou plus résistantes à l'usure.
- Lors de l'usinage de trous en plusieurs étapes, commencez par les trous les plus grands, puis traitez les trous plus petits.
- Veillez à ce que la pression du liquide de refroidissement soit suffisante pour rincer les copeaux pendant le perçage en U.
- Ne pas mélanger les plaquettes pour le centre et la périphérie des forets U, sinon la tige du foret U risque d'être endommagée.
- Lors du perçage avec un foret en U, la rotation de la pièce, la rotation de l'outil ou la rotation simultanée peuvent être utilisées, mais l'avance linéaire est généralement utilisée avec la rotation de la pièce.
- Tenez compte des capacités de la machine pendant l'usinage CNC et ajustez les paramètres de coupe de manière appropriée, en réduisant généralement les vitesses et les avances.
U Paramètres de forage
Calcul des paramètres d'usinage pour les forets en U (perçage rapide)
Calcul de la vitesse de rotation du foret
n = (Vc × 1000) / (3,14 × Dc)
Vc (m/min) : Valeur standard de la vitesse linéaire
Dc (mm) : Diamètre du foret
n (tr/min) : vitesse réelle du foret
Exemple : Si la vitesse linéaire de la plaquette est de 100 m/min et que le diamètre du foret est de 20 mm, la vitesse de rotation du foret est : n = (100 × 1000) / (3.14 × 20) ≈ 1600rev/min
Détermination de la vitesse d'avance
Vf = Fr × n
Vf (mm/min) : vitesse d'avance de l'outil
Fr (mm/rev) : vitesse d'avance par tour
n (tr/min) : vitesse de rotation de la broche
Exemple : Si la vitesse de la broche est de 1600 tr/min et que l'avance par tour est de 0,1 mm/tour, la vitesse d'avance est la suivante : Vf = Fr × n = 1600 × 0,1 = 160mm/min
Estimation du temps d'usinage des trous
Tc = (H / Vf) × 60
Tc (s) : temps nécessaire à l'usinage
H (mm) : Profondeur du trou
Exemple : Percez un trou d'un diamètre de 20 mm et d'une profondeur de 40 mm, si la vitesse d'avance est de 140 mm/min, alors le temps d'usinage est : Tc = (H / Vf) × 60 = (40 / 160) × 60 ≈ 15s
Vitesse de coupe du foret U
Il est essentiel de déterminer la vitesse de coupe correcte des forets U pour obtenir des performances et une durée de vie optimales. Les vitesses de coupe des forets U sont généralement plus élevées que celles des forets conventionnels en raison de leur conception avancée et de la technologie des plaquettes.
Les facteurs qui influencent la vitesse de coupe des forets U sont les suivants :
- Dureté et composition des matériaux
- Diamètre du foret
- Qualité et géométrie de l'insert
- Type de liquide de refroidissement et méthode de distribution
En règle générale, la vitesse de coupe des forets U pour l'acier est comprise entre 300 et 600 pieds de surface par minute (SFM), tandis que la vitesse pour l'aluminium peut être nettement plus élevée, dépassant souvent 1000 SFM. Il convient de toujours se référer aux recommandations du fabricant et de les adapter en fonction de l'application spécifique et des résultats souhaités.
u types de forets
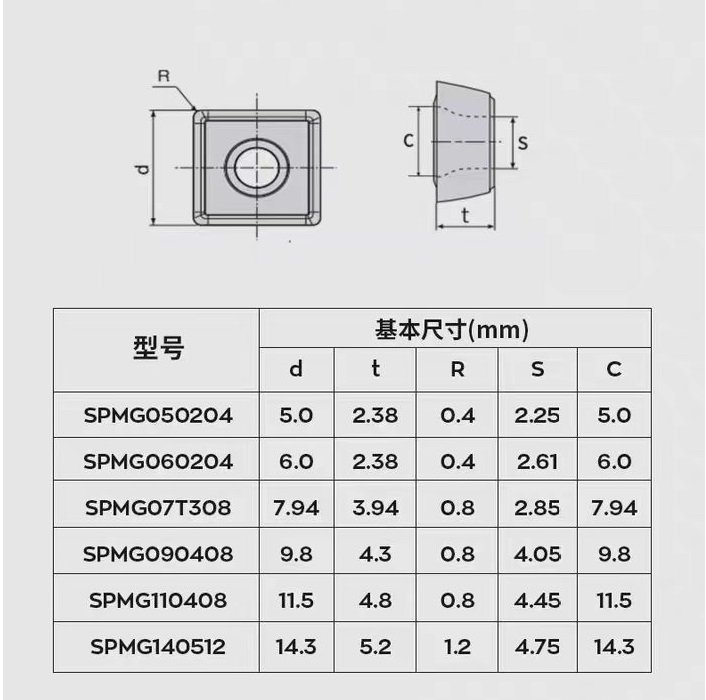
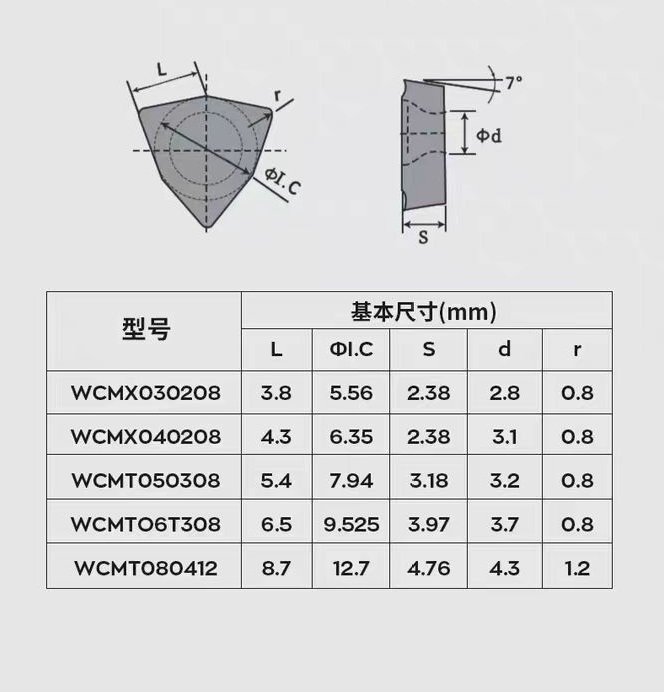
Types de forets U, notamment :insert spmg(spmg 05 insert, spmg 06 insert, spmg 07 insert, spmg 09 insert, spmg 11 insert, spmg 14 insert) et wcmx insert (wcmx 03 insert, wcmx 04 insert, wcmx 05 insert, wcmx 06 insert, wcmx 08 insert).
Forets en U CNC
L'intégration des forets U aux machines CNC (Computer Numerical Control) a révolutionné le processus de perçage dans la fabrication moderne. Les perceuses en U à commande numérique offrent plusieurs avantages par rapport aux opérations de perçage manuel :
- Précision et répétabilité accrues
- Productivité accrue grâce à l'automatisation des changements d'outils
- Capacité à réaliser des schémas et des séquences de forage complexes
- Amélioration du contrôle et de la surveillance des processus
Lors de l'utilisation de la CNC Exercices en UIl est important de prendre en compte des facteurs tels que
- Sélection correcte du porte-outil
- Compensation précise de la longueur et du diamètre de l'outil
- Programmation CNC optimisée pour des trajectoires d'outils efficaces
Forets en U pour VMC (centres d'usinage verticaux)
Les centres d'usinage verticaux (VMC) sont des machines polyvalentes qui peuvent grandement bénéficier de l'utilisation de forets en U. Lorsque vous utilisez des forets U pour des applications VMC, tenez compte des points suivants :
- Rigidité de la machine et maintien de la pièce
- Capacités du système de distribution du liquide de refroidissement
- Exigences en matière de changement d'outil pour différentes tailles de trous
- Intégration avec d'autres opérations d'usinage
Les forets U destinés aux applications VMC présentent souvent des adaptations spéciales pour maximiser les performances dans les orientations verticales, telles que des canaux d'arrosage améliorés et des géométries de plaquettes optimisées pour l'évacuation des copeaux assistée par la gravité.
Choisir le bon foret en U
Le choix du foret en U approprié à votre application spécifique est crucial pour obtenir des résultats optimaux. Tenez compte des facteurs suivants lors du choix d'un foret en U :
- Exigences en matière de diamètre et de profondeur des trous
- Propriétés des matériaux
- Capacités des machines
- Volume de production
- Exigences en matière de finition de surface
- Considérations relatives au coût (investissement initial ou économies à long terme)
Consultez des experts en outillage et des fabricants pour vous assurer que vous choisissez le foret en U qui répond le mieux à vos besoins et maximise votre efficacité d'usinage.
Points importants pour l'utilisation de la foreuse en U
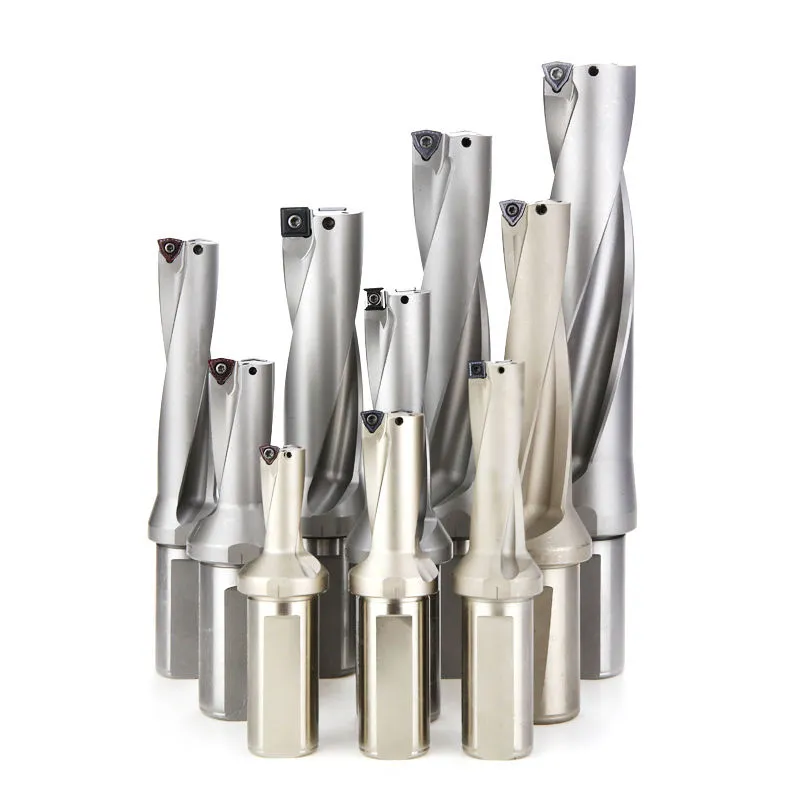

- Veillez à ce que l'installation se fasse dans le bon sens, c'est-à-dire que les inserts soient orientés vers le haut, vers le bas, vers l'intérieur ou vers l'extérieur.
- La hauteur du centre doit être calibrée dans une plage de contrôle de 0,1 mm en fonction du diamètre. Les forets en U de petit diamètre ont des exigences plus élevées en matière de hauteur de centre. Une hauteur de centre incorrecte peut entraîner une usure irrégulière de la plaquette, des trous surdimensionnés et une réduction de la durée de vie de la plaquette.
- Les foreuses en U ont des exigences élevées en matière de liquide de refroidissement - le liquide de refroidissement doit atteindre le centre et la pression est meilleure lorsqu'elle est élevée. Les orifices excédentaires de liquide de refroidissement peuvent être obstrués pour garantir la pression.
- Suivre les considérations du fabricant en matière de paramètres de coupe, mais aussi tenir compte des différentes marques de plaquettes et de la puissance de la machine. Prenez en compte la charge de la machine pendant l'usinage et procédez aux ajustements nécessaires, généralement en utilisant des vitesses élevées et des avances réduites.
- Inspecter et remplacer les inserts en temps voulu. Ne pas inverser les inserts.
- Réglez la profondeur de coupe en fonction de la dureté de la pièce et de la longueur de dépassement de la plaquette. Les pièces plus dures nécessitent des longueurs de surplomb plus importantes et des profondeurs de coupe plus faibles.
- N'utilisez pas de plaquettes trop usées. Enregistrez l'usure des plaquettes par rapport aux quantités de pièces usinables et remplacez les plaquettes en temps voulu.
- Utiliser un liquide de refroidissement interne adéquat et correctement pressurisé. Ses fonctions principales sont l'élimination des copeaux et le refroidissement.
- Les forets U ne conviennent pas aux matériaux plus tendres comme le bronze pourpre ou l'aluminium tendre.
Maintenance et entretien des foreuses en U
Un bon entretien des foreuses U est essentiel pour garantir leur longévité et des performances constantes. Suivez ces bonnes pratiques :
- Inspecter régulièrement les inserts pour vérifier qu'ils ne sont pas usés ou endommagés
- Nettoyer et lubrifier le corps du foret et les inserts
- Stocker les forets U dans un environnement propre et sec
- Suivre les directives du fabricant pour l'indexation et le remplacement des plaquettes
- Contrôler les paramètres de coupe et les ajuster si nécessaire pour éviter une usure prématurée
Dépannage des problèmes courants liés aux foreuses U :
- Mauvaise qualité du trou : Vérifier l'état de la plaquette et les paramètres de coupe
- Vibrations excessives : Vérifier l'équilibre du porte-outil et la rigidité de la machine.
- Taille de trou incohérente : Vérifier l'usure de la plaquette ou une mauvaise configuration
Conclusion
Les forets U sont devenus un outil indispensable dans les opérations d'usinage modernes, car ils offrent des performances et une efficacité supérieures dans un large éventail d'applications. En comprenant les tableaux de tailles de forets U, les paramètres et les meilleures pratiques, les machinistes peuvent tirer parti de ces outils polyvalents pour obtenir des résultats exceptionnels dans leurs opérations de perçage.
Au fur et à mesure que la technologie progresse, on peut s'attendre à de nouvelles innovations dans la conception, les matériaux et les revêtements des forets U. Ces développements permettront probablement d'obtenir des vitesses de coupe encore plus élevées, une meilleure résistance à l'usure et des applications plus étendues pour les forets U. Ces développements conduiront probablement à des vitesses de coupe encore plus élevées, à une meilleure résistance à l'usure et à un élargissement des applications des forets U à l'avenir.
En maîtrisant l'utilisation des forets U et en restant informés des dernières avancées en matière de technologie de perçage, les machinistes et les fabricants peuvent conserver un avantage concurrentiel dans le monde en constante évolution de l'usinage de précision.
Qu'est-ce qu'un foret en U et en quoi diffère-t-il d'un foret hélicoïdal classique ?
Un foret en U est un foret à plaquettes indexables dont la goujure est en forme de U, offrant une meilleure évacuation des copeaux et des vitesses de coupe plus élevées que les forets hélicoïdaux traditionnels. Il utilise des plaquettes en carbure remplaçables au lieu d'une arête de coupe solide.
Quels matériaux peuvent être usinés avec un foret en U ?
Les forets en U peuvent usiner une large gamme de matériaux, notamment l'acier, l'acier inoxydable, la fonte, l'aluminium et d'autres métaux non ferreux. Ils conviennent également pour certains matériaux composites.
Quels sont les avantages de l'utilisation d'un foret en U ?
Les avantages comprennent des vitesses de coupe plus élevées, une meilleure qualité de trou, une meilleure évacuation des copeaux, une durée de vie plus longue de l'outil et la possibilité de remplacer facilement les plaquettes usées plutôt que l'ensemble du foret.
Comment choisir la bonne taille de foret U ?
Consultez le tableau des dimensions des forets en U fourni par le fabricant. Tenez compte du diamètre et de la profondeur du trou requis, du matériau à percer et des spécifications de votre machine.
Quelles sont les vitesses de coupe typiques des forets U ?
Les vitesses de coupe varient en fonction du matériau et de la taille du foret, mais elles sont généralement comprises entre 300 et 600 SFM pour l'acier et peuvent dépasser 1000 SFM pour l'aluminium. Toujours se référer aux recommandations du fabricant.
Les forets U peuvent-ils être utilisés dans les machines CNC ?
Oui, les forets U sont couramment utilisés dans les machines CNC, y compris les centres d'usinage verticaux (VMC). Ils s'intègrent bien aux processus automatisés.
u drill devir ilerleme?
Devir (vitesse de rotation) : La vitesse de rotation, ou vitesse de la broche, est généralement mesurée en tours par minute (tr/min). Pour les foreuses U, la vitesse de rotation optimale dépend de plusieurs facteurs :
Matériau à percer : Des matériaux différents nécessitent des vitesses de coupe différentes.
Diamètre du foret U : Les diamètres plus importants nécessitent généralement des vitesses de rotation plus faibles.
Vitesse de coupe du foret U : elle est généralement indiquée par le fabricant en pieds de surface par minute (SFM) ou en mètres par minute (m/min).
Pour calculer le régime approprié, utilisez la formule suivante : RPM = (SFM x 3,82) / Diamètre (en pouces)
İlerleme (vitesse d'avance) : La vitesse d'avance est la vitesse à laquelle le foret pénètre dans la pièce, généralement mesurée en pouces par tour (IPR) ou en millimètres par tour (mm/rev).
Les facteurs qui influencent la vitesse d'alimentation sont les suivants :
Dureté du matériau
Qualité de trou souhaitée
Taille du foret U
Rigidité de la machine
Les fabricants de forets en U indiquent généralement les vitesses d'avance recommandées pour les différents matériaux et tailles de forets.