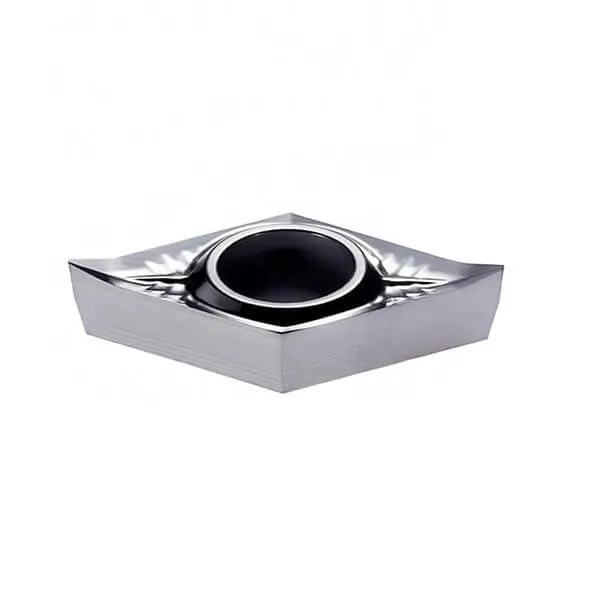
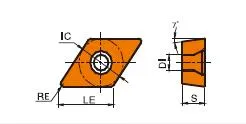
DCGT insert
DCGT insert angle:7° Positive rake insert with a single-sided Chipbreaker;
55° Rhombic turning insert;
Primary workpiece material: Aluminium;
Breaker application: Semi-finshing and finishing machining;
Matching turning tool holder: SDQCR/L, SDUCR/L;
DCGT insert dimensions:DCGT0702/DCGT11T3;
Material : Tungsten carbide;
DCGT insert specification
Finishing geometry with high positive rake face for chip control in long chipping materials.
DCGT insert tool holder


DCGT insert Introduction
- D: Shape. Rhombic (diamond) with a 55-degree included angle.
- C : Clearance Angle. 7 degrees (positive).
- G: Tolerance. Medium (‘G’) is standard, though other precision tolerances exist.
- T: Chipbreaker style & Hole Configuration. This letter designates the specific chipbreaker geometry and whether the insert has a hole or not. Chipbreaker variations are numerous and manufacturer-specific.
- Chiffres numériques :
- Deux premiers chiffres : Inscribed circle (IC) diameter in millimeters. To obtain the approximate inch equivalent, divide this number by 25.4.
- Prochain Deux Chiffres : Thickness in millimeters. Divide by 25.4 to convert to inches.
- Last Two Digits: Nose radius in millimeters. To convert to inches, divide by 25.4.
DCGT Insert Dimensions (ISO)
| Désignation ISO | Cercle inscrit (CI) | Épaisseur | Rayon de l'angle |
|---|---|---|---|
| DCGT 070202 | 7.94mm (0.313") | 2.38mm (0.094") | 0.2mm (0.008") |
| DCGT 070204 | 7.94mm (0.313") | 2.38mm (0.094") | 0,4 mm (0,016") |
| DCGT 11T302 | 11mm (0.433") | 3.18mm (0.125") | 0.2mm (0.008") |
| DCGT 11T304 | 11mm (0.433") | 3.18mm (0.125") | 0,4 mm (0,016") |
| DCGT 11T308 | 11mm (0.433") | 3.18mm (0.125") | 0,8 mm (0,031") |
Example: DCGT 11T308
- Rhombic (diamond) shape with a 55-degree included angle
- 7-degree positive clearance angle
- Medium tolerance
- Manufacturer-specific chipbreaker and hole configuration
- 11mm inscribed circle diameter (approx. 0.43″ in inches)
- 3.18mm thick (approx. 0.125″ in inches)
- Rayon de nez de 0,8 mm (environ 0,031″ en pouces)
La science derrière les plaquettes en carbure : Comment elles sont fabriquées et pourquoi elles sont si résistantes
Les plaquettes en carbure comptent parmi les outils de coupe les plus polyvalents et les plus durables qui soient. Mais comment sont-elles fabriquées ? Et qu'est-ce qui les rend si résistantes ? Dans cette vidéo, nous allons explorer la science des plaquettes en carbure, des propriétés du carbure de tungstène au processus de fabrication.
Notre capacité de production











