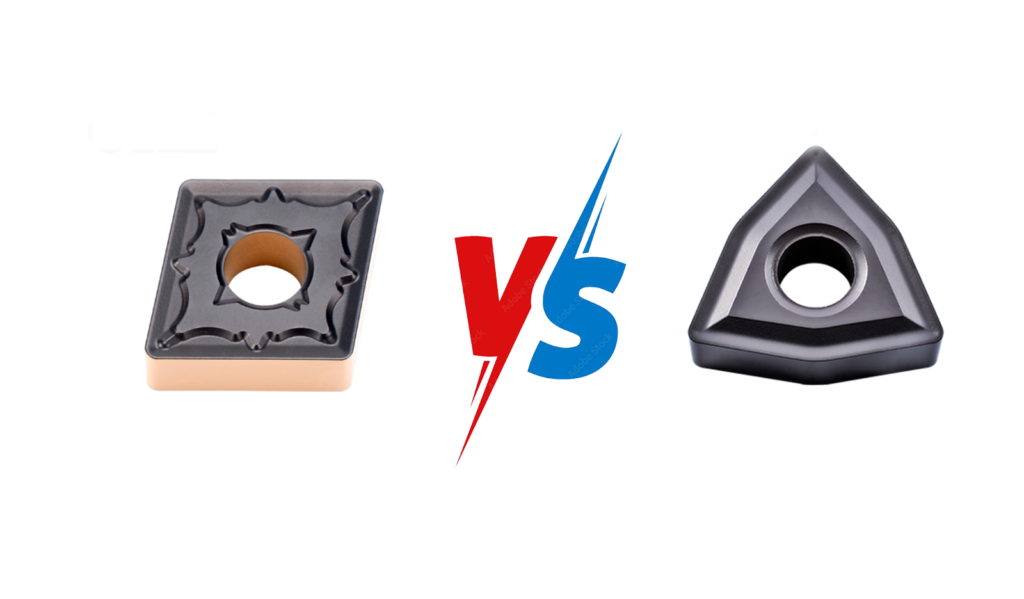
CNMG VS WNMG 是車削加工中常用的兩種刀片。雖然它們有相似之處,但也有不同的特性,因此適用於不同的應用。
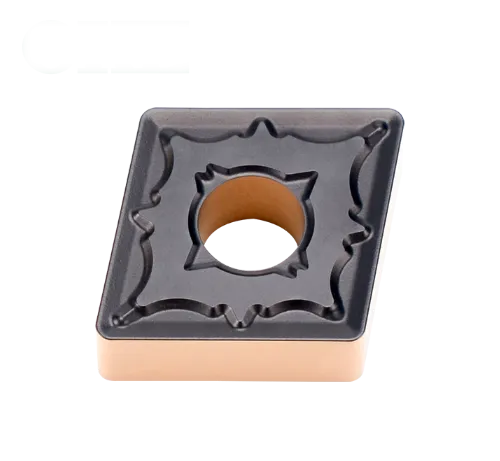
CNMG 嵌件
- Shape and Design: Rhombic (diamond-shaped) with an 80° corner angle, 0° (neutral) clearance angle, and double-sided, providing 4 cutting edges.
- Strengths:
- Robustness: The 80° corner angle and secure pocket design in the toolholder make CNMG inserts ideal for heavy roughing and high-feed-rate operations. They handle tough materials and interrupted cuts well due to their strong cutting edge.
- 多樣性: Suitable for both turning and facing without repositioning the toolholder, making them efficient for job-shop work or roughing/facing combined operations.
- Rigidity: The CNMG’s pocket design offers greater stability, reducing insert movement and improving accuracy, especially in heavy cuts.
- Availability: More common, with a wider range of grades, chipbreakers, and coatings, making them easier to source and often cheaper.
- Weaknesses:
- Fewer cutting edges (4 vs. 6 for WNMG), which may increase cost per edge in high-volume operations.
- May chatter slightly on light finishing cuts compared to other inserts like TNMG.
- 應用:
- Best for roughing operations, machining tough materials (e.g., stainless steel, cast iron, high-temperature alloys), and jobs requiring high material removal rates.
- Preferred for larger parts or heavy-duty CNC and manual lathes with sufficient horsepower.

WNMG 嵌件
- Shape and Design: Trigon-shaped (six-sided) with an 80° corner angle, 0° clearance angle, and double-sided, offering 6 cutting edges.
- Strengths:
- 成本效益: Six cutting edges reduce the cost per edge, making WNMG inserts economical for general-purpose turning, especially in high-volume production.
- Good Finish: WNMG inserts often provide better surface finishes in medium to finishing cuts due to their geometry, especially with smaller nose radii (e.g., 0.4–0.8 mm).
- 晶片控制: The trigon shape can offer improved chip clearance, reducing chip buildup in certain applications.
- Weaknesses:
- Less Rigid: The WNMG’s pocket design has less bearing surface, making it less stable for heavy roughing. Toolholder pockets may wear faster (“wholler out”), leading to insert movement and reduced accuracy.
- Not Ideal for Heavy Cuts: Less robust than CNMG for aggressive machining or tough materials due to the trigon shape’s reduced edge strength.
- Limited Holder Availability: Smaller WNMG toolholders (e.g., for 1/2″ shanks) are harder to find, often requiring 5/8″ or larger shanks, which may not suit smaller lathes.
- 應用:
- Best for medium to light cuts, finishing operations, and general-purpose turning on softer materials or smaller parts.
- Suitable for shops prioritizing economy and where heavy roughing isn’t required.
主要差異
| 特點 | CNMG | WNMG |
|---|---|---|
| 形狀 | Rhombic (80° angle) | Trigon (80° angle) |
| 切邊 | 4 (double-sided) | 6 (double-sided) |
| 強度 | Stronger, better for roughing | Less robust, better for finishing |
| Toolholder Rigidity | More secure pocket, less wear | Less secure, prone to pocket wear |
| 應用 | Heavy roughing, tough materials | Medium/light cuts, finishing |
| Cost per Edge | Higher (fewer edges) | Lower (more edges) |
| Availability | More common, wider variety | Less common, fewer options |

When to Choose
- Choose CNMG:
- For roughing operations or heavy material removal.
- When machining tough materials like stainless steel or cast iron.
- If you need a versatile insert for combined turning and facing.
- For machines with sufficient power and rigidity (e.g., larger CNC lathes).
- Choose WNMG:
- For finishing or medium cuts where surface finish is critical.
- In high-volume production where cost per edge matters.
- On smaller or less powerful lathes (though ensure toolholder compatibility).
- When chip control is a priority in lighter cuts.
Practical Considerations
- Machine Power: Both are negative rake inserts, requiring more horsepower than positive rake inserts (e.g., CCMT). Smaller lathes (<10″ swing) may struggle, so consider positive rake inserts like CCMT or TCMT for low-power machines.
- Toolholder Wear: WNMG toolholders wear faster due to less pocket support, so inspect regularly to maintain accuracy.
- Material and Chipbreaker: Match the insert grade and chipbreaker to your material (e.g., stainless steel needs specific coatings). CNMG has more grade options.
- 成本: WNMG’s extra edges may save money in high-volume setups, but CNMG’s durability can offset costs in heavy-duty applications.
Recommendation
- For job shops 或 heavy roughing, CNMG is the go-to due to its strength, versatility, and availability.
- For finishing 或 cost-sensitive production, WNMG is better, especially if you can manage toolholder wear and don’t need aggressive cuts.
- Always verify your lathe’s horsepower and toolholder compatibility, especially for WNMG on smaller machines.
If you have specific materials, machine details, or operations in mind, I can tailor the recommendation further!