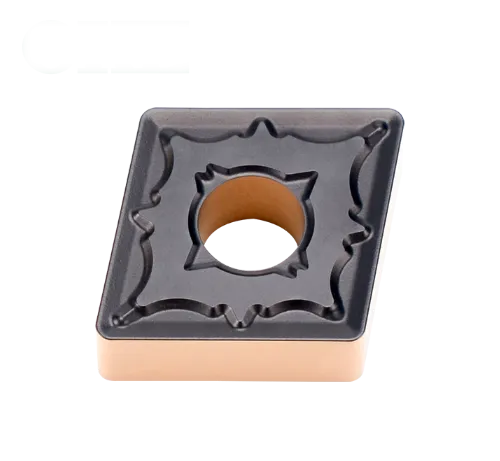

CNMG داخل کریں۔
CNMG insert angle:0° Negative rake insert with double-sided chipbreaker;
80° rhombic turning insert;
Primary workpiece material: the best cnmg insert for stainless steel, brass, bronze, aluminium and cast iron ;
Breaker application: rough, heavy, semi-finshing;
Matching cnmg insert tool holder: PCBNR/L, PCLNR/L, MCLNR/L,MCBNR/L;
Grade: Both PVD and CVD;
Material : Tungsten carbide;
CNMG insert can deal with multiple operations by combining different chip breakers and grades.
CNMG insert specification
The CNMG Insert dimensions have four major categories which are (ISO standard)CNMG120404, CNMG120408, CNMG120412, and CNMG190616;(ANSI standard)CNMG332,CNMG431,CNMG432,CNMG433,CNMG543,CNMG643.
The multiple types of dimensions enable to meet different customer requirements and working conditions.
CNMG insert tool holder



MCLNR/L
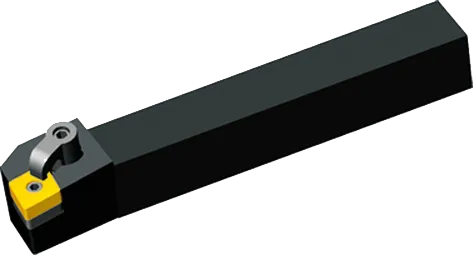
CNMG insert Introduction
CNMG Inserts: The Essentials
- Shape: Rhombic (diamond) with an 80-degree included angle.
- Clearance Angle: 0 degrees.
- Cutting Edges: Double-sided, offering two cutting edges per insert for cost-effectiveness.
- Chipbreaker Geometries: A wide range of chipbreaker styles from various manufacturers, tailored to specific materials and machining operations (roughing, finishing, etc.).
- Key Uses: Ideal for a variety of turning operations, including facing and profiling, on a wide range of workpiece materials.
Common Materials CNMG Inserts are Used For
- Steels: Various steel grades, including carbon and alloy steels.
- Stainless Steels: CNMG inserts can effectively machine different stainless steel types.
- Cast Iron: Suitable for many cast iron applications.
- Some High-Temperature Alloys: Depending on the specific alloy and grade.
Advantages of CNMG Inserts
- Cost-Effective: Due to their double-sided design and wide availability.
- Versatile: An extensive range of grades and chipbreakers make them suitable for many machining applications.
- Good Chip Control: Well-designed chipbreakers ensure effective chip flow and protect the workpiece, tool, and machine.
- Strong Geometric Shape: The 80-degree diamond shape provides strength and rigidity for various cutting scenarios.
Important Considerations
- Match the Grade to Your Material: Choosing the right insert coating and substrate composition is crucial for optimal tool life and performance in the specific material you’re cutting.
- Select the Right Chipbreaker: The chipbreaker geometry significantly influences how chips are formed and broken. It should be chosen based on the material and type of machining operation.
- Machine Rigidity: Ensure your machine has enough power and rigidity to handle the cutting forces CNMG inserts can generate.
CNMG Insert Dimensions (ISO)
| ISO Designation | Inscribed Circle (IC) | موٹائی | Corner Radius |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNMG 120404 | 12.7mm (0.5") | 4.76mm (0.187") | 0.4mm (0.016") |
| CNMG 120408 | 12.7mm (0.5") | 4.76mm (0.187") | 0.8mm (0.031") |
| CNMG 120412 | 12.7mm (0.5") | 4.76mm (0.187") | 1.2mm (0.047") |
| CNMG 160608 | 16mm (0.63") | 6.35mm (0.25") | 0.8mm (0.031") |
| CNMG 160612 | 16mm (0.63") | 6.35mm (0.25") | 1.2mm (0.047") |
| CNMG 190612 | 19.05mm (0.75") | 6.35mm (0.25") | 1.2mm (0.047") |
Example: CNMG 120408
- 12: Inscribed Circle (IC) of 12.7mm (approx. 0.5 inches)
- 04: Thickness of 4.76mm (approx. 0.187 inches)
- 08: Corner radius of 0.8mm (approx. 0.031 inches)
Key Dimensions
Inscribed Circle (IC): The diameter of the largest circle that fits within the insert. Common IC sizes include:
- 12.7mm (0.5″)
- 16mm (0.63″)
- 19.05mm (0.75″)
موٹائی: Impacts insert strength and the number of usable cutting edges. Common thicknesses include:
- 3.18mm (0.125″)
- 4.76mm (0.187″)
- 6.35mm (0.25″)
Corner Radius: Affects surface finish and strength at the cutting edge. Common sizes include:
- 0.4mm (0.016″)
- 0.8mm (0.031″)
- 1.2mm (0.047″)
F.A.Q.
Shape:
TNMG: Triangular insert with a 60-degree included angle.
CNMG: Diamond-shaped insert with an 80-degree included angle.
Cutting Edge Strength:
TNMG: Triangular inserts with six cutting edges are very stable and are suitable for roughing and semi-finishing operations.
CNMG:Compared with TNMG insert, it has 8 cutting edges, which is more economical; the top angle of 80 degrees has more stability; it is suitable for roughing and semi-finishing.
1. Shape: CNMG inserts are diamond-shaped indexable cutting tool inserts with an included angle of 80 degrees.
2. Material: They are usually made from tungsten carbide, which is very hard and wear-resistant. CNMG inserts can often have coatings added to enhance their performance, like wear resistance or improved chip flow.
3. Usage: CNMG inserts are used in turning operations on lathes to shape and cut materials like steel, stainless steel, cast iron, and non-ferrous metals.
4. Mounting: The inserts are held securely in a toolholder, providing multiple cutting edges.
CNMG insert geometry :
• C: Diamond shape (80-degree included angle)
• N: Negative rake angle (usually provides a stronger cutting edge)
• M: Medium tolerance class (a general purpose tolerance for fit and precision)
• G: Ground finish (indicates the surface of the insert has been ground for accuracy)
Advantages of CNMG Inserts:
• Strength: The diamond shape and 80-degree angle provide four robust cutting edges, making them great for heavier machining.
• Versatility: They can be used for various turning operations like roughing, semi-finishing, and even some finishing work.
• Cost-effective: Multiple cutting edges per insert improve their lifespan and reduce tooling costs.
Yes, a CNMG 543 insert is thicker than a CNMG 433 insert. Here’s why:
In a CNMG designation, the third digit in the size code represents the insert thickness.
- CNMG 433: The “3” indicates a thickness of 3/16″.
- CNMG 543: The “5” indicates a thickness of 5/16″.
Therefore, the CNMG 543 is thicker than the CNMG 433.
Let me know if you’d like to compare any other insert thicknesses!
Choosing the best CNMG insert grade for 4340 steel depends on several factors, including:
آپریشن کی قسم:
- Roughing: Requires an insert grade with high toughness and wear resistance to withstand heavy cutting forces and chip loads.
- Finishing: Prioritizes surface finish, so a harder, finer-grained grade is better. You’ll need to balance this with wear resistance.
Specific 4340 Properties:
- Heat Treatment: Has the 4340 been hardened? Harder 4340 will require even tougher insert grades, possibly with special coatings.
Here are some commonly recommended CNMG insert grades for 4340, along with their strengths:
General-Purpose Grades:
- CVD Coated Grades (e.g., PVD TiAlN): Offer good balance of toughness and wear resistance for roughing and semi-finishing.
- PVD Coated with Alumina (Al2O3) layer: Provides better heat resistance, good for higher speeds in 4340 with moderate hardness.
Finishing-Focused Grades
- Fine-Grained Uncoated Grades: For improved surface finish in softer 4340, but wear faster.
- CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride): Super-hard material for excellent finish on hardened 4340, but more expensive and brittle.
Popular Insert Manufacturers and Grade Examples
- Sandvik Coromant: GC4415, GC4425 (CVD coated grades versatile for 4340)
- Kennametal: KCP25B, KC5010 (good for hardened 4340)
- Walter: WPP10S, WPP20S (general-purpose, good starting point)
- Mitsubishi: UE6110 (uncoated fine grain for finishing)
Important Considerations
- چپ بریکر اسٹائل: Match the chipbreaker to your operation and the 4340’s hardness to manage chip formation and avoid cutting edge damage.
- Coolant: Proper coolant use is essential, especially for harder 4340 workpieces.
Recommendation:
Start with a versatile CVD-coated grade suitable for your 4340 steel’s hardness. Always consult manufacturer data sheets and machining recommendations for your specific insert grade.
Let me know if you have details on the following, and I can give you a more tailored insert grade recommendation:
- Type of turning operation (roughing, finishing)
- Hardness of your 4340 material
- Any specific surface finish requirements
Yes, a CNMG 543 insert does have a defined thickness. Here’s how to understand it:
In the CNMG designation, the third number in the size code represents the insert’s thickness in sixteenths of an inch.
- CNMG 543: The “5” represents a thickness of 5/16″ of an inch.
Let me know if you’d like to know the thickness of other CNMG inserts or have a specific comparison in mind!
The Science Behind Carbide Inserts: How They're Made and Why They're So Strong
Carbide inserts are some of the most versatile and durable cutting tools available. But how are they made? And what makes them so strong? In this video, we’ll explore the science behind carbide inserts, from the properties of tungsten carbide to the manufacturing process.
Our Production Capability











