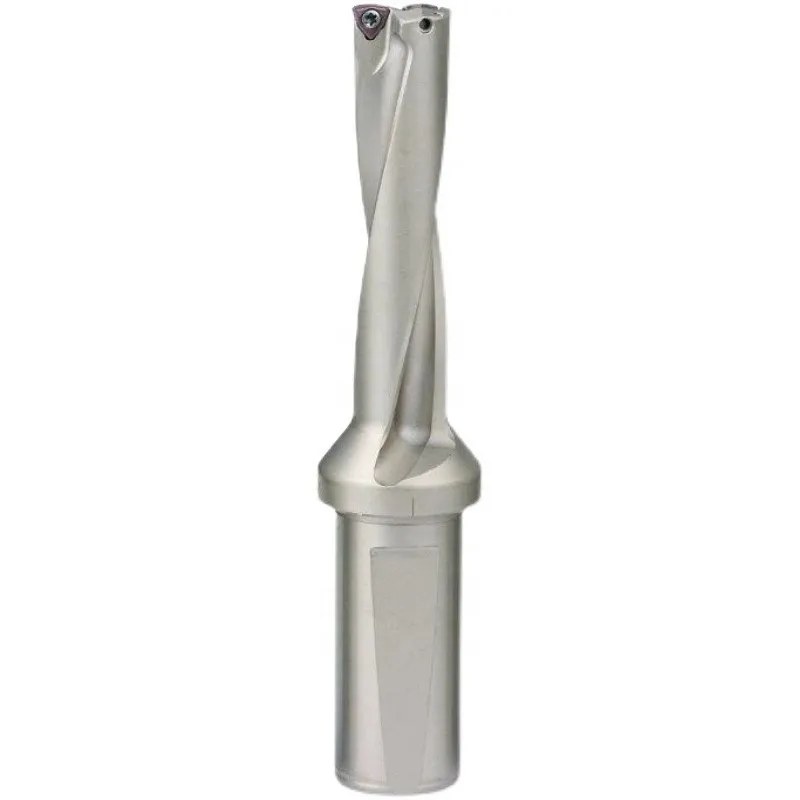
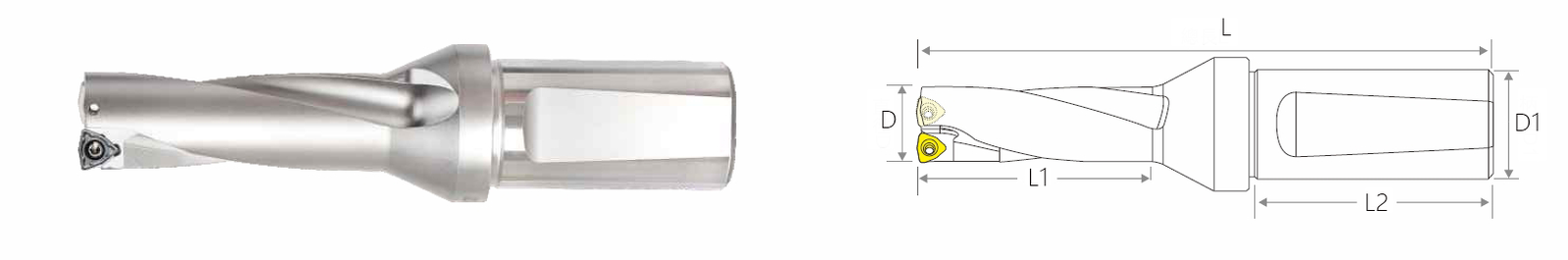
SP 시리즈 인서트가 있는 U 드릴 2D 바디 20mm 섕크
1. SP 시리즈 카바이드 인서트 사용
2. 2D U 드릴 바디
3. H13 강철을 원료로 사용합니다. 담금질 후 가공, 높은 경도, 우수한 강성, 손상되기 쉽지 않습니다.
4. 이중 나선형 냉각 구조, 더 긴 인서트 수명.
- 인덱서블 카바이드 인서트: 이것이 결정적인 특징입니다. U 드릴은 교체 가능한 카바이드 인서트를 절삭 날로 사용합니다. 이러한 인서트는 일반적으로 여러 개의 절삭 포인트를 가지고 있으며 마모되면 개별적으로 회전하거나 교체할 수 있으므로 전체 드릴 비트를 다시 연마하거나 교체할 필요가 없습니다. 따라서 다운타임과 툴링 비용이 크게 줄어듭니다.
- U자형 플루트 디자인: 플루트의 독특한 U자 모양은 효율적인 칩 배출에 최적화되어 있습니다. 이 디자인은 절삭 영역에서 칩을 부드럽고 빠르게 제거하여 칩이 쌓이는 것을 방지하고 특히 깊은 홀에서 공구 파손의 위험을 줄여줍니다.
- 툴 관통형 냉각수 채널: 대부분의 U 드릴은 절삭날에 직접 냉각수를 공급하는 내부 채널로 설계되어 있습니다. 이는 효과적인 냉각과 윤활을 제공하여 열을 제어하고 마찰을 줄이며 칩 배출을 개선하고 인서트 공구 수명을 연장하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
- 리지드 툴 바디: 드릴 본체는 일반적으로 경화강으로 제작되어 드릴링 과정에서 높은 강성과 안정성을 제공합니다. 이러한 강성 덕분에 기존 드릴에 비해 절삭 속도와 이송 속도가 빨라져 생산성이 향상됩니다.
- 듀얼 커팅 엣지: U 드릴은 일반적으로 중앙 인서트와 주변 인서트의 두 가지 인서트를 사용합니다. 이 구성은 균형 잡힌 절삭력을 보장하고 향상된 진원도와 직진도를 포함하여 더 나은 홀 품질에 기여합니다.
- 셀프 센터링 기능: U 드릴의 설계는 종종 셀프 센터링 효과를 제공하여 많은 응용 분야에서 미리 드릴링된 중심 구멍 없이도 공작물에 직접 드릴링을 시작할 수 있습니다.
- 다용도성: 다양한 인서트 형상과 재종을 사용할 수 있는 U 드릴은 강철, 스테인리스강, 주철, 알루미늄 및 기타 비철금속을 포함한 다양한 소재를 가공하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 향상된 홀 품질: 견고한 바디, 효과적인 칩 배출, 정밀한 인서트의 조합으로 치수 정확도, 표면 마감 및 직진도가 향상된 홀이 생성되므로 보링 또는 리밍과 같은 2차 마감 작업이 필요 없거나 줄어드는 경우가 많습니다.
| 모델 번호 | (L1/D) | (L1) | (L) | (D) | D1/L2 | 삽입 | 나사 | 렌치 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP02-2D-8.5-C20A | 2D | 17 | 85 | 8.5 | 20/50 | SPMG020102 | M1.8×3.2L | T6 |
| SP02-2D-9-C20A | 2D | 18 | 86 | 9 | 20/50 | |||
| SP02-2D-9.5-C20A | 2D | 19 | 87 | 9.5 | 20/50 | |||
| SP04-2D-10-C20A | 2D | 20 | 88 | 10 | 20/50 | SPMG040202 | M1.8×4.0L | |
| SP04-2D-10.5-C20A | 2D | 21 | 89 | 10.5 | 20/50 | |||
| SP04-2D-11-C20A | 2D | 22 | 89.5 | 11 | 20/50 | |||
| SP04-2D-11.5-C20A | 2D | 23 | 90 | 11.5 | 20/50 | |||
| SP04-2D-12-C20A | 2D | 24 | 91 | 12 | 20/50 | SPMG040202 SPMG040204 | M1.8×4.0L | |
| SP04-2D-12.5-C20A | 2D | 25 | 92 | 12.5 | 20/50 | M2.0x5.5L | ||
| SP05-2D-13-C20A | 2D | 26 | 93 | 13 | 20/50 | SPMG05D204 | M2.2×5.5L | |
| SP05-2D-13.5-C20A | 2D | 27 | 94 | 13.5 | 20/50 | |||
| SP05-2D-14-C20A | 2D | 28 | 95 | 14 | 20/50 | |||
| SP05-2D-14.5-C20A | 2D | 29 | 96 | 14.5 | 20/50 | |||
| SP05-2D-15-C20A | 2D | 30 | 97 | 15 | 20/50 | |||
| SP05-2D-15.5-C20A | 2D | 31 | 98 | 15.5 | 20/50 | |||
| SP05-2D-16-C20A | 2D | 32 | 99 | 16 | 20/50 | |||
| SP05-2D-16.5-C20A | 2D | 33 | 100 | 16.5 | 20/50 | |||
| SP05-2D-17-C20A | 2D | 34 | 101 | 17 | 20/50 | |||
| SP05-2D-17.5-C20A | 2D | 35 | 102 | 17.5 | 20/50 | |||
| SP05-2D-18-C20A | 2D | 36 | 103 | 18 | 20/50 | |||
| SP05-2D-18.5-C20A | 2D | 37 | 104 | 18.5 | 20/50 | |||
| SP06-2D-19-C20A | 2D | 38 | 105 | 19 | 20/50 | SPMG060204 | M2.5x6L | T8 |
| SP06-2D-19.5-C20A | 2D | 39 | 106 | 19.5 | 20/50 | |||
| SP06-2D-20-C20A | 2D | 40 | 107 | 20 | 20/50 | |||
| SP06-2D-20.5-C20A | 2D | 41 | 108 | 20.5 | 20/50 | |||
| SP06-2D-21-C20A | 2D | 42 | 109 | 21 | 20/50 | |||
| SP06-2D-21.5-C20A | 2D | 43 | 110 | 21.5 | 20/50 | |||
| SP06-2D-22-C20A | 2D | 44 | 111 | 22 | 20/50 | |||
| SP06-2D-22.5-C20A | 2D | 45 | 112 | 22.5 | 20/50 | |||
| SP07-2D-23-C20A | 2D | 46 | 113 | 23 | 20/50 | SPMG07T308 | M2.5x7L | |
| SP07-2D-23.5-C20A | 2D | 47 | 114 | 23.5 | 20/50 | |||
| SP07-2D-24-C20A | 2D | 48 | 115 | 24 | 20/50 |