SNMA insert
SNMA carbide insert angle: 90° Square carbide insert; 0° Negative Rake Insert and No Chipbreaker;
90°Square carbide Insert for wide range of materials;
Breaker Application: Roughing machining;
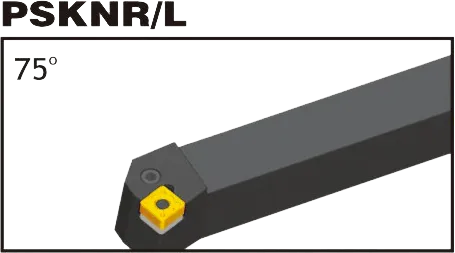
Matching SNMA Tool Holder: MSKNR/L,MSDNN,MSBNR/L,PSBNR/L,PSDNN,PSKNR/L;
SNMA Insert can deal with multiple operations by combining different chip breakers and grades;
Materiale: carburo di tungsteno;
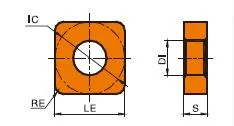
Specifiche
SNMA carbide inserts have 4 cutting edges per side. If the insert is negative then it is possible to use a total of 8 corners.
In this case, it makes this style of insert very economical.
It has a cutting edge angle of 90° so it has high cutting edge strength.
Normally, the insert dimension depends on the needs of customers and the space for the cutting tools in the application.
In addition, the Indexable Carbide Insert has gone through various processes such as quenching to improve its performance.
The surface has been treated with a special coating, thus it gains the properties of corrosion resistance and rustproof.
What’s more, it has the properties of good positioning accuracy, high hardness, long service life, wear resistance, corrosion resistance as well as cost effective.
The Indexable Carbide Insert is widely applied in metal turning, milling, cutting and grooving, thread turning, etc.
SNMA insert Meaning
Understanding the SNMA Insert Code
- S: Forma: Quadrato
- N: Clearance Angle: Negative
- M: Tolleranza: La tolleranza media è standard, ma possono essere disponibili altre tolleranze di precisione.
- A: Stile del rompitruciolo e configurazione del foro. Questa lettera indica la geometria specifica del rompitruciolo e se l'inserto ha un foro o meno. Le varianti del rompitruciolo sono numerose e specifiche del produttore.
- Cifre numeriche:
- Le prime due cifre: Diametro del cerchio inscritto (IC) in millimetri. Per ottenere l'equivalente approssimativo in pollici, dividere questo numero per 25,4.
- Successivo Due cifre: Spessore in millimetri. Dividere per 25,4 per convertire in pollici.
- Ultime due cifre: Raggio d'angolo in millimetri. Per convertire in pollici, dividere per 25,4.
SNMA insert holder





SNMA carbide Insert Dimensions (ISO)
| Designazione ISO | Cerchio iscritto (IC) | Spessore | Raggio d'angolo |
|---|---|---|---|
| SNMA 090308 | 9,52 mm (0,375") | 3,18 mm (0,125") | 0,8 mm (0,031") |
| SNMA 120404 | 12,7 mm (0,5") | 4,76 mm (0,187") | 0,4 mm (0,016") |
| SNMA 120408 | 12,7 mm (0,5") | 4,76 mm (0,187") | 0,8 mm (0,031") |
| SNMA 120412 | 12,7 mm (0,5") | 4,76 mm (0,187") | 1,2 mm (0,047") |
| SNMA 150412 | 15.875mm (0.625") | 4,76 mm (0,187") | 1,2 mm (0,047") |
| SNMA 190612 | 19,05 mm (0,75") | 6,35 mm (0,25") | 1,2 mm (0,047") |
Example: SNMA 120408
- Forma quadrata
- Angolo di sicurezza negativo
- Tolleranza media
- Configurazione del rompitruciolo e del foro specifica del produttore
- 12.7mm inscribed circle diameter (approx. 0.5″ in inches)
- 4,76 mm di spessore (circa 0,187″ in pollici)
- Raggio d'angolo di 0,8 mm (circa 0,031″ in pollici).
La scienza degli inserti in metallo duro: Come sono fatti e perché sono così forti
Gli inserti in metallo duro sono tra gli utensili da taglio più versatili e durevoli che esistano. Ma come sono fatti? E cosa li rende così resistenti? In questo video esploreremo la scienza alla base degli inserti in metallo duro, dalle proprietà del carburo di tungsteno al processo di produzione.
La nostra capacità di produzione











