U drill, one of the most commonly used tools for hole processing, is usually called by different names, such as shallow hole drill, water jet drill, violent drill, fast drill, T-drill, insert drill, etc. The standard name should be indexable insert drill or machine chuck drill. The term “U-drill” originates from the Sandvik Coromant T-MAX U-drill, which was then widely circulated in the industry and gradually evolved into a common name.
What are the types of inserts used in U-drills?
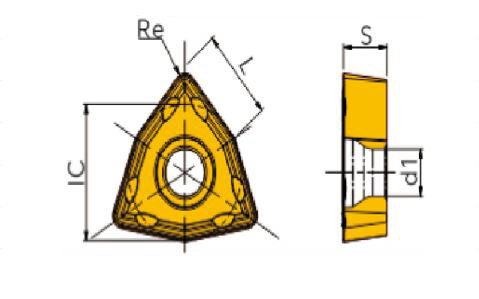
There are several common types of SPMG, SOMT, WCMT, WCMX, the specific data can refer to the following table.

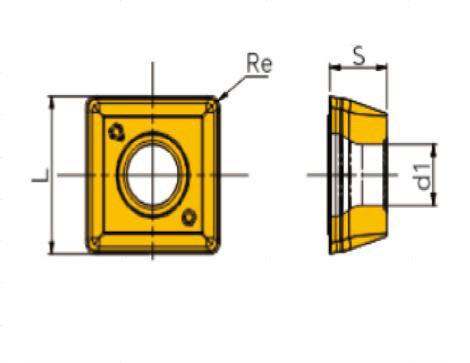
| Model | L | S | 關於 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOMT050204-PC FPA010 | 4.9 | 2.38 | 0.4 |
| SOMT060204-PC FPA010 | 5.7 | 2.38 | 0.4 |
| SOMT070306-PC FPA010 | 6.8 | 2.8 | 0.6 |
| SOMT08T306-PC FPA010 | 7.9 | 3.97 | 0.6 |
| SOMT09T308-PC FPA010 | 9.2 | 3.97 | 0.8 |
| SOMT11T308-PC FPA010 | 11 | 3.97 | 0.8 |
| SOMT130408-PC FPA010 | 12.8 | 4.4 | 0.8 |
| SOMT150510-PC FPA010 | 15 | 4.8 | 1 |
| Model | L | S | 關於 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPMG050204-EC FPA010 | 5 | 2.38 | 0.4 |
| SPMG060204-EC FPA010 | 6 | 2.38 | 0.4 |
| SPMG07T308-EC FPA010 | 7.94 | 3.97 | 0.8 |
| SPMG090408-EC FPA010 | 9.8 | 4.3 | 0.8 |
| SPMG110408-EC FPA010 | 11.5 | 4.8 | 0.8 |
| SPMG140512-EC FPA010 | 14.3 | 5.2 | 1.2 |
| Model | L | 我知道了 | S | 關於 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WCMT030208-TM FPA005 | 3.8 | 5.56 | 2.38 | 0.8 |
| WCMT040208-TM FPA005 | 4.3 | 6.35 | 2.38 | 0.8 |
| WCMT050308-TM FPA010 | 5.4 | 7.94 | 3.18 | 0.8 |
| WCMT06T308-TM FPA010 | 6.5 | 9.525 | 3.97 | 0.8 |
| WCMT080412-TM FPA010 | 8.7 | 12.7 | 4.76 | 1.2 |
Types WC, SP and SO are the most commonly used U演練 inserts in metalworking. Drilling operations are well suited for the use of indexable insert drills because they reduce the time required for tool changes. The technique of using u drills as roughing is very successful. Deeper cavities or holes can be created by making multiple axial cuts with a drill or milling cutter. This method is particularly suitable for roughing. Since the main cutting forces are concentrated axially along the spindle, it is energy-efficient, effective and reduces the requirements on the machine spindle. Drilling holes for the insert drilling tool is the first step in the internal insert milling process. The unique chipbreaker has a one-of-a-kind design incorporating corrugated edges. This ensures both high edge strength and effective chipbreaking.
Tips for machining with U drill inserts
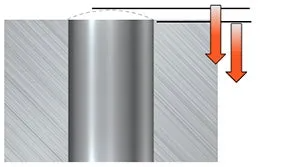
不規則表面鑽孔
不規律的
凸面
凹
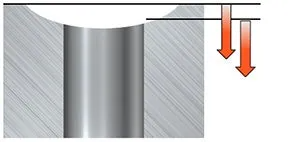
- 盡可能使用最短的鑽頭,以最大限度地減少振動趨勢並減少偏轉的影響
- 切削速度的建議起始值和建議的最低進給量
- 當凹面半徑等於或小於鑽頭半徑時,不建議使用 6–7×DC
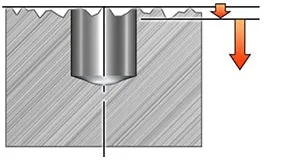
預鑽孔

為了使中心和周邊刀片之間的切削力平衡在可接受的水平上,預鑽孔不應大於DC/4
跨孔鑽
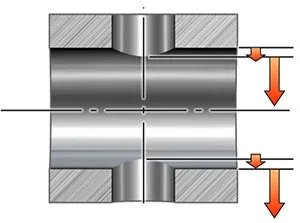
Challenges:
- Chip evacuation is affected, might become more problematic
- Deburring in the crossing is hard. Burr formation must be as small as possible
- Causes more tool wear than conventional drilling
Guidelines:
- 對於不同直徑的孔:先鑽較大的孔以減少毛邊的形成
- 在過孔期間從建議的最低進給開始
- 不建議用於長切屑材料,因為在穿過孔洞時會排屑
Drilling inclined entrances/exits
Generates uneven and excessive forces acting on the cutting edges
- Intermittent cutting as the drill enters/exits the workpiece
- Increases chance of vibration
- Can distort the drilling profile
- Causes more tool wear than conventional drilling
General recommendations:
- Stability is crucial. A small length to diameter ratio will help to keep the tolerances
- Milling a small flat surface is recommended when entering workpieces with a large inclination
成角度或傾斜的表面、入口
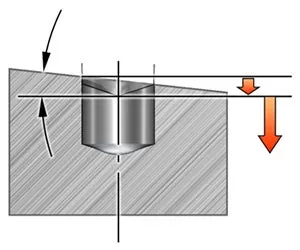
- 盡可能使用最短的鑽頭,以最大限度地減少振動趨勢並減少偏轉的影響
- 從建議的最低切削速度和建議的最低進給量的 1/3(或更低)開始,直到完全嚙合,然後返回正常進給量
- 4–5×DC 傾斜入口的角度最大可達 15°
- 6–7×DC 傾斜入口的角度最大可達 10°
有角度或傾斜的表面,出口
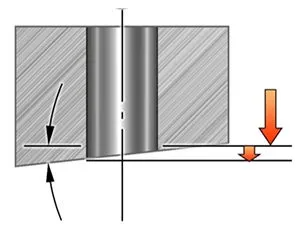
- 盡可能使用最短的鑽頭,以最大限度地減少振動趨勢並減少偏轉的影響
- 切削速度的建議起始值和建議的最低進給量(或更低)
- 4–5×DC 傾斜出口的角度最大可達 15°
- 6–7×DC 傾斜出口的角度最大可達 5°
不對稱曲面鑽孔

- 使用盡可能短的鑽頭,以盡量減少鑽頭從中心向外的彎曲,類似於傾斜表面
- 對於凹面,將進給量減少至初始鑽進速度的 1/3
- 曲面半徑應大於鑽頭半徑
- 不建議用於 6–7×DC 鑽頭
How U drill inserts work and what applications they have
The U drill, also known as a drill with indexable inserts, is a tool primarily used for high-efficiency hole drilling in various materials. Below is a detailed explanation of how a U drill works:
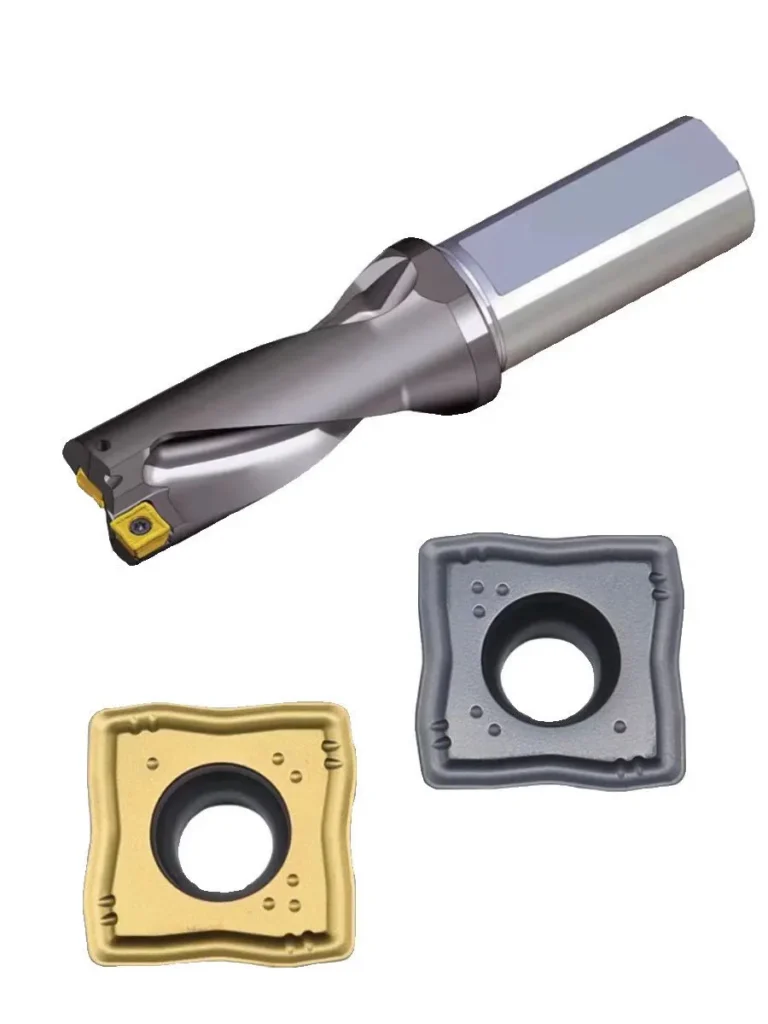

1. Components and Structure
- U Drill Body: This is the main part of the U drill, typically made from a robust material. It has two insert seats: one near the center and one at the periphery. These seats hold the replaceable inserts (cutting edges).
- Inserts: U drills use two indexable inserts: the center insert 和 peripheral insert. The center insert cuts the material at the core of the hole, while the peripheral insert cuts the outer edges. The outer insert generally does more work as it handles a larger cutting surface.
2. Cutting Process
- Dual Cutting Action: As the U drill rotates at high speeds, both inserts engage the workpiece simultaneously. The center insert cuts the inner part of the hole, and the outer insert cuts the outer diameter. This combination makes the U drill highly efficient because the cutting load is distributed across two inserts.
- Coolant System: U drills are typically designed with internal coolant channels. Coolant flows through these channels and directly cools the cutting zone, reducing heat and friction. It also helps to flush chips out of the drilled hole.
3. Drilling Operation
- Alignment and Positioning: Before drilling, the workpiece is firmly clamped on the machine table or fixture. The U drill’s center is aligned with the intended hole location, either through CNC programming or manual positioning.
- Initiating the Cut: The machine spindle rotates, and the U drill begins to move into the workpiece. The center insert starts the cutting by drilling the core, followed closely by the peripheral insert. As the tool penetrates deeper, both inserts continue to remove material efficiently.
- Chip Evacuation: As material is cut away, chips are generated. These chips are expelled from the hole by the combined action of the rotating inserts and the internal coolant, which helps clear the chips and prevents clogging.
- Completion of Drilling: Once the U drill reaches the programmed depth, the tool retracts, leaving behind a finished hole. Due to the high precision of the inserts and the tool body design, the hole is usually accurate and requires no further reworking.
4. Advantages of U Drills
- High Efficiency: Since the U drill uses two inserts to cut simultaneously, it operates at much higher speeds and feeds compared to traditional drills, reducing cycle time.
- Precision: The design of the U drill ensures accurate hole diameters, often eliminating the need for additional finishing operations like boring or reaming.
- Coolant Efficiency: The built-in coolant channels keep the inserts cool during high-speed drilling, reducing wear and extending tool life.
5. Operating Considerations
- Insert Selection: It’s essential to choose the right insert material and geometry based on the workpiece material (e.g., steel, aluminum, cast iron). Using the correct inserts ensures smoother cuts and prolongs tool life.
- Cutting Parameters: The drilling speed and feed rate should be adjusted according to the material and depth of the hole. If the feed rate is too high, it can cause excessive wear or damage to the inserts.
- Coolant Flow: Ensure the coolant system is properly set up and functioning. Insufficient coolant can lead to overheating and premature tool failure.
What Are U Drill Inserts and Why Are They Popular?
U drill inserts are cutting tools used in indexable U drills, specifically designed for high-efficiency hole drilling. These inserts are typically made from carbide or other hard materials, which are capable of withstanding high cutting speeds and temperatures. They are replaceable, meaning once an insert becomes dull, you can swap it out instead of replacing the entire drill, making them cost-effective.
why U drill inserts are popular:
High Efficiency: U drills with inserts can drill holes much faster than traditional twist drills because they cut using two inserts simultaneously—one for the hole center and one for the perimeter. This reduces machining time significantly.
Cost-Effective: Since the inserts are replaceable, the overall tooling cost is reduced. Instead of replacing an entire drill, you only need to replace the worn inserts.
Versatility: U drill inserts can be used on various materials such as steel, stainless steel, cast iron, and non-ferrous materials. Different insert geometries and coatings are available to suit different applications.
Precision: U drill inserts provide high precision when drilling, often creating holes with minimal need for secondary finishing operations like boring or reaming.
Coolant Delivery: Many U drills are designed with internal coolant channels that cool the inserts during drilling, improving tool life and chip evacuation.
Important Considerations When Using U Drill Inserts
To ensure optimal performance when using U drill inserts, several factors need to be taken into account:
1. Insert Material Selection
Choose the correct insert material (carbide, coated carbide, etc.) based on the workpiece material. Different materials require specific inserts to achieve the best results. For instance, tougher inserts may be needed for drilling through hard steels, while softer materials like aluminum may require a more specialized insert geometry.
2. Cutting Speed and Feed Rate
The cutting speed and feed rate should be appropriate for the workpiece material and insert type. Excessive feed rates can cause insert failure, while too low feed rates may result in poor chip formation or excessive heat buildup.
Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for recommended speeds and feeds, adjusting based on material hardness and depth of hole.
3. Coolant Management
Ensure that coolant is properly directed to the cutting zone. Coolant helps to reduce heat, prevent tool wear, and aid in chip evacuation. U drills often come with internal coolant channels, but you must ensure these channels are functioning correctly.
Using insufficient coolant or having a blocked coolant passage can lead to overheating, reduced tool life, and poor hole quality.
4. Proper Insert Installation
Make sure the inserts are properly seated and secured in the U drill body. Improper installation can lead to insert shifting, poor hole quality, or even damage to the tool body.
Periodically check for insert wear and replace inserts when they are dull to avoid damaging the workpiece or tool.
5. Chip Evacuation
Monitor chip evacuation during the drilling process. Poor chip removal can cause chips to clog the hole, leading to tool failure, overheating, or workpiece damage.
Adjust feed rates or coolant flow if chips are not being effectively removed from the hole.
6. Hole Depth and Accuracy
U drills are ideal for producing holes quickly, but accuracy can vary depending on the setup and material. For deep holes, ensure proper alignment of the U drill to avoid deviation, which can lead to tapered or out-of-round holes.
7. Insert Wear Monitoring
Keep track of insert wear during use. Worn inserts can negatively affect hole quality and may also cause excess heat, increasing the risk of breakage or damage to the workpiece.
Regular inspections and timely insert changes are essential to maintain hole quality and extend tool life.
By following these guidelines and using the right insert for the application, you can maximize the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and precision of U drills in your machining operation
結論
The U-drill is a drilling tool containing carbide inserts characterized by ease of use and cost-effectiveness. In order to facilitate the machining of a wide range of materials, ONMY U-drill inserts are available in a variety of types and sizes.ONMY U-drill inserts offer an energy-saving and efficient solution, in addition to a high metal removal rate. For high quality U-drill inserts, contact ONMY! Contact us and we will be happy to answer any questions or concerns you may have.