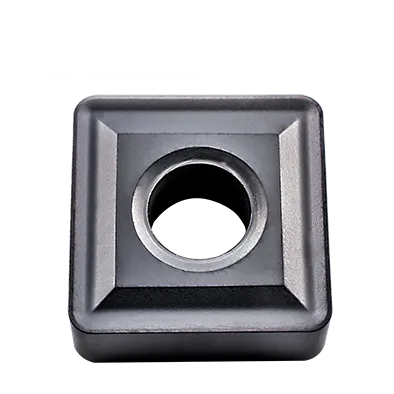
SNMG داخل کریں۔
SNMG insert angle: 90° Square , 0° Negative Rake Insert with double-sided Chipbreaker;
90°Square carbide Insert for wide range of materials;
Breaker Application: Available in a range of radius for finishing, general purpose and rough turning;
Range of SNMG insert types:SNMG432/SNMG543/SNMG643;
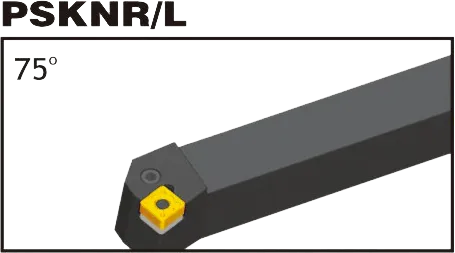
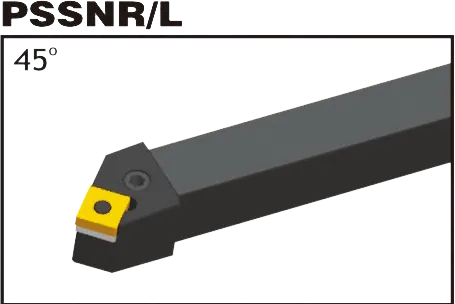
Matching SNMG insert Tool Holder: DSBNR/L, PSBNR/L, PSDNN, PSKNR/L, PSSNR/L, MSBNR/L, MSRNR/L, MSKNR/L, MSDNN;
SNMG Insert can deal with multiple operations by combining different chip breakers and grades;
Material : Tungsten Carbide;
Features
Double-Sided Cutting Edges: SNMG inserts offer multiple cutting edges on both sides, increasing their cost-effectiveness.
Chipbreakers: SNMG inserts often come with various chipbreaker geometries designed to improve chip control and surface finish in different materials and machining operations.
Coatings: Inserts are frequently coated with materials like TiN, TiCN, and Al2O3 for better wear resistance, heat tolerance, and optimal performance in different materials.
Typical Applications of SNMG Inserts.
SNMG insert Meaning
S: Square shape with a 90-degree included angle. This shape provides strength and stability to the cutting edge.
N: Negative rake angle. This refers to the angle at which the cutting edge meets the workpiece. A negative rake angle creates a stronger cutting edge, suitable for heavier cuts and harder materials.
M: Medium tolerance class. This indicates a general-purpose range of precision, making these inserts suitable for various machining applications.
G: Ground finish. This means the insert’s surfaces have been ground for accuracy and dimensional consistency.
SNMG inserts are versatile and used in various turning applications, including:
Roughing: Their strong cutting edge and negative rake angle make them suited for heavy material removal.
Semi-Finishing: They can provide a decent balance between strength and surface finish for semi-finishing operations.
General-purpose Turning: Their versatility makes them a popular choice for general machining of various materials.
Suitable Materials
SNMG inserts are often used to machine:
Steel
Stainless steel
Cast Iron
Some non-ferrous metals (depending on the specific insert grade)
SNMG insert tool holder






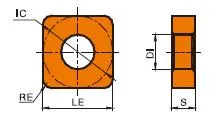
SNMG carbide Insert Dimensions (ISO and INCH)
| ISO Designation | INCH Designation | Inscribed Circle (IC) | موٹائی | Corner Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNMG 090304 | SNMG 321 | 9.52mm (0.375") | 3.18mm (0.125") | 0.4mm (0.016") |
| SNMG 090308 | SNMG 322 | 9.52mm (0.375") | 3.18mm (0.125") | 0.8mm (0.031") |
| SNMG 120404 | SNMG 431 | 12.7mm (0.5") | 4.76mm (0.187") | 0.4mm (0.016") |
| SNMG 120408 | SNMG 431 | 12.7mm (0.5") | 4.76mm (0.187") | 0.8mm (0.031") |
| SNMG 120412 | SNMG 433 | 12.7mm (0.5") | 4.76mm (0.187") | 1.2mm (0.047") |
| SNMG 190612 | SNMG 643 | 19.05mm (0.75") | 6.35mm (0.25") | 1.2mm (0.047") |
SNMG inserts come in various sizes, corner radii, and other specifications. The most common variations include:
SNMG 1204 and SNMG 1906 are among the most widely used sizes.
12 or 19: Indicates an Inscribed Circle (IC) of 12mm or 19mm (approximate). The IC determines the overall size of the insert.
04, 06, 08, 12: Indicates the thickness (e.g., 0.157″ or 4mm for 04)
02, 04, 08: Indicates the corner radius (e.g., 0.031″ or 0.8 mm for 04). Larger radii provide a stronger cutting edge, while smaller radii offer a better surface finish.
The Science Behind Carbide Inserts: How They're Made and Why They're So Strong
Carbide inserts are some of the most versatile and durable cutting tools available. But how are they made? And what makes them so strong? In this video, we’ll explore the science behind carbide inserts, from the properties of tungsten carbide to the manufacturing process.
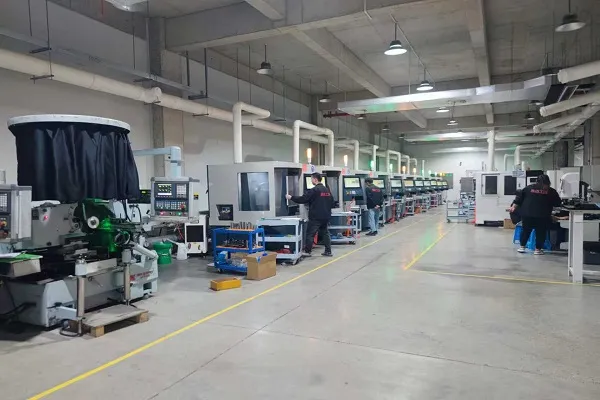
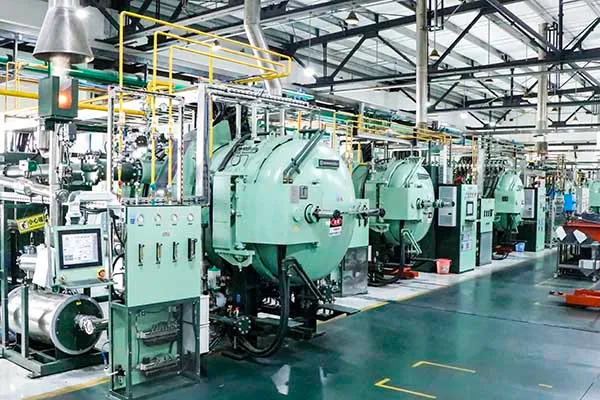
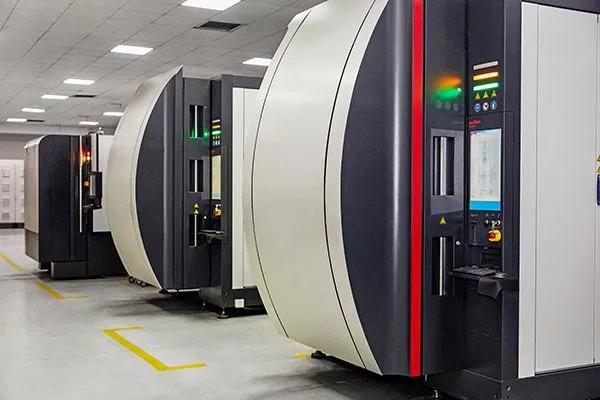
Our Production Capability











