SNMA داخل کریں۔
SNMA carbide insert angle: 90° Square carbide insert; 0° Negative Rake Insert and No Chipbreaker;
90°Square carbide Insert for wide range of materials;
Breaker Application: Roughing machining;
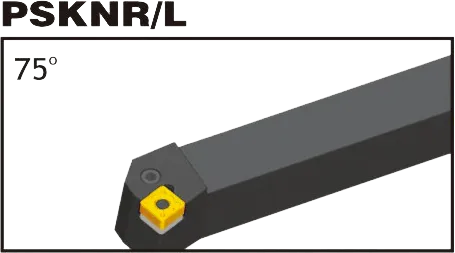
Matching SNMA Tool Holder: MSKNR/L,MSDNN,MSBNR/L,PSBNR/L,PSDNN,PSKNR/L;
SNMA Insert can deal with multiple operations by combining different chip breakers and grades;
Material : Tungsten Carbide;
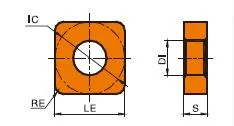
Specification
SNMA carbide inserts have 4 cutting edges per side. If the insert is negative then it is possible to use a total of 8 corners.
In this case, it makes this style of insert very economical.
It has a cutting edge angle of 90° so it has high cutting edge strength.
Normally, the insert dimension depends on the needs of customers and the space for the cutting tools in the application.
In addition, the Indexable Carbide Insert has gone through various processes such as quenching to improve its performance.
The surface has been treated with a special coating, thus it gains the properties of corrosion resistance and rustproof.
What’s more, it has the properties of good positioning accuracy, high hardness, long service life, wear resistance, corrosion resistance as well as cost effective.
The Indexable Carbide Insert is widely applied in metal turning, milling, cutting and grooving, thread turning, etc.
SNMA insert Meaning
Understanding the SNMA Insert Code
- S: Shape: Square
- N: Clearance Angle: Negative
- M: Tolerance: Medium tolerance is standard, though other precision tolerances might be available.
- A: Chipbreaker style & Hole Configuration. This letter designates the specific chipbreaker geometry and whether the insert has a hole or not. Chipbreaker variations are numerous and manufacturer-specific.
- Numerical Digits:
- First Two Digits: Inscribed circle (IC) diameter in millimeters. To obtain the approximate inch equivalent, divide this number by 25.4.
- Next Two Digits: Thickness in millimeters. Divide by 25.4 to convert to inches.
- Last Two Digits: Corner radius in millimeters. To convert to inches, divide by 25.4.
SNMA insert holder





SNMA carbide Insert Dimensions (ISO)
| ISO Designation | Inscribed Circle (IC) | موٹائی | Corner Radius |
|---|---|---|---|
| SNMA 090308 | 9.52mm (0.375") | 3.18mm (0.125") | 0.8mm (0.031") |
| SNMA 120404 | 12.7mm (0.5") | 4.76mm (0.187") | 0.4mm (0.016") |
| SNMA 120408 | 12.7mm (0.5") | 4.76mm (0.187") | 0.8mm (0.031") |
| SNMA 120412 | 12.7mm (0.5") | 4.76mm (0.187") | 1.2mm (0.047") |
| SNMA 150412 | 15.875mm (0.625") | 4.76mm (0.187") | 1.2mm (0.047") |
| SNMA 190612 | 19.05mm (0.75") | 6.35mm (0.25") | 1.2mm (0.047") |
Example: SNMA 120408
- Square shape
- Negative clearance angle
- Medium tolerance
- Manufacturer-specific chipbreaker and hole configuration
- 12.7mm inscribed circle diameter (approx. 0.5″ in inches)
- 4.76mm thick (approx. 0.187″ in inches)
- 0.8mm corner radius (approx. 0.031″ in inches).
The Science Behind Carbide Inserts: How They're Made and Why They're So Strong
Carbide inserts are some of the most versatile and durable cutting tools available. But how are they made? And what makes them so strong? In this video, we’ll explore the science behind carbide inserts, from the properties of tungsten carbide to the manufacturing process.
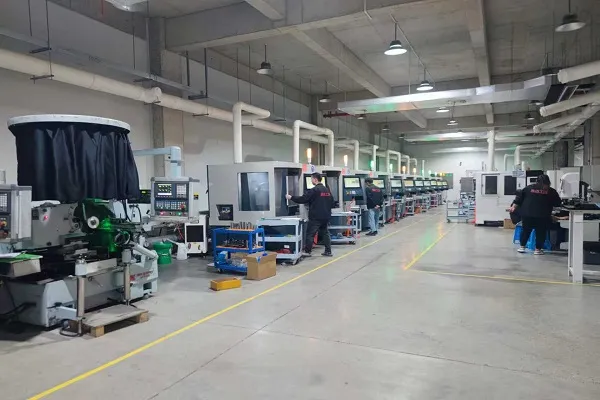
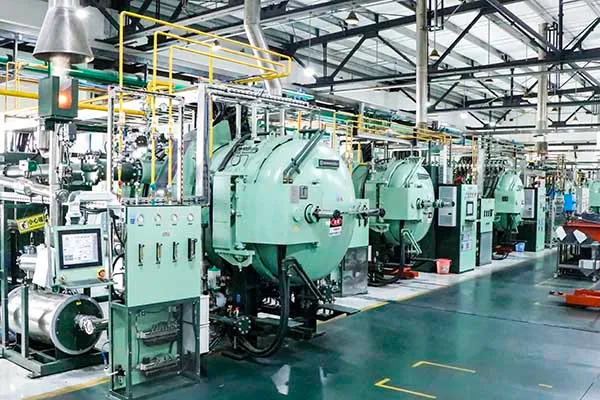
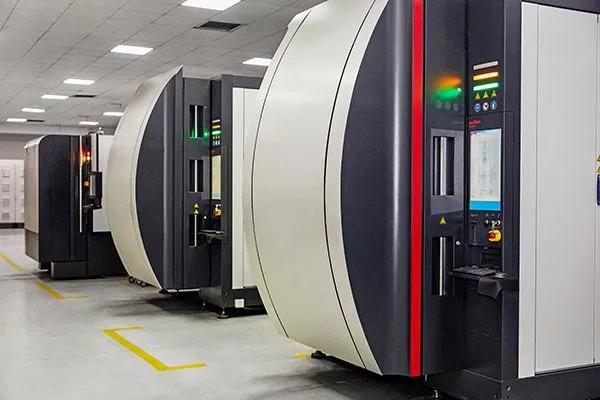
Our Production Capability











