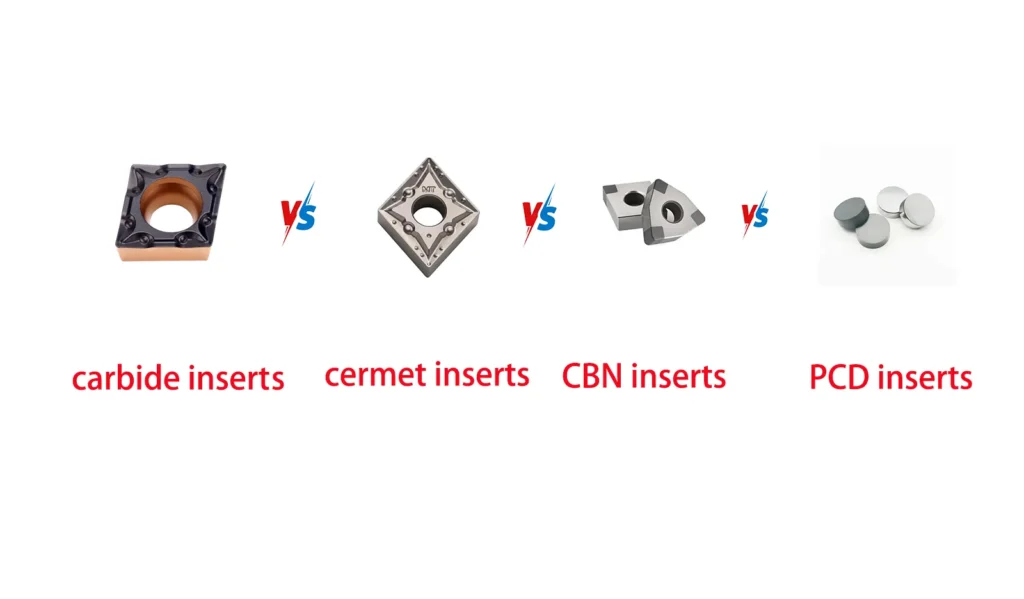
サーメットインサート vs 超硬合金 vs CBN vs PCD
機械加工と金属加工の世界では、最適な性能、効率、費用対効果を達成するために、適切な切削工具材料を選択することが極めて重要です。この包括的なガイドでは、サーメットチップ、超硬、立方晶窒化ホウ素(CBN)、多結晶ダイヤモンド(PCD)切削工具の主な違いについて説明します。各材料のユニークな特性、用途、およびコストに関する考慮事項を理解することで、加工ニーズに対して十分な情報に基づいた決定を下すことができるようになります。
1.はじめに材料科学の最先端
切削工具の材料に関して言えば、サーメットチップと超硬、CBN、PCDの比較は、機械加工や製造のプロにとって不可欠です。これらの材料には、それぞれ異なる利点と制限があり、異なる用途や被削材に適しています。この記事では、これらの切削工具材料の複雑さを掘り下げ、複雑な機械加工の世界を自信を持ってナビゲートできるようにします。
2.サーメットインサート:両方の長所
組成と特性
セラミック」と「金属」の合成語であるサーメットインサートは、セラミック材料の硬度と金属バインダーの靭性を兼ね備えています。一般的に炭化チタン(TiC)または炭窒化チタン(TiCN)の粒子をニッケルベースの合金で結合したサーメットインサートは、ユニークな特性のバランスを提供します。
メリットとデメリット
メリット
- 超硬合金よりも高い耐摩耗性
- 優れた熱安定性
- 優れた表面仕上げ能力
- 良好な化学的安定性
デメリット
- 超硬合金に比べて靭性が低い
- 超硬チップより脆い
- 超硬合金に比べ、入手性が限られる
アプリケーション
サーメット製インサートは、以下の点で優れている:
- 鋼鉄および鋳鉄の仕上げ作業
- 軟質材料の高速加工
- 優れた表面仕上げを必要とする用途
3.超硬インサート:万能の主力工具
組成と特性
超硬チップ超硬合金としても知られるこの材料は、コバルトマトリックスと結合した炭化タングステン(WC)粒子で構成されています。この組成により、硬度と靭性を兼ね備えた材料となり、幅広い加工用途に適している。
メリットとデメリット
メリット
- 優れた硬度と靭性のバランス
- 用途に応じて幅広いグレードを用意
- 優れた耐摩耗性
- 多くの加工工程で費用対効果が高い
デメリット
- セラミックスや超硬材料に比べて低い熱間硬度
- 特定の用途では、性能向上のためにコーティングが必要な場合がある
アプリケーション
超硬チップは広く使用されている:
- 各種材料の汎用加工
- フライス加工、旋盤加工、穴あけ加工
- 荒加工と中仕上げ加工
4.立方晶窒化ホウ素(CBN):鋼のスペシャリスト
組成と特性
立方晶窒化ホウ素(CBN)は、ダイヤモンドに次ぐ硬度を持つ合成超硬材料である。六方晶窒化ホウ素を高温高圧にかけることで立方晶の結晶構造になる。
メリットとデメリット
メリット
- 極めて高い硬度と耐摩耗性
- 優れた熱安定性
- 焼入れ鋼の加工で優れた性能
- 鉄系材料加工時の化学的安定性
デメリット
- 超硬合金やサーメットに比べて高コスト
- 脆いため、取り扱いや塗布に注意が必要
- 柔らかい素材への効果は限定的
アプリケーション
CBNが得意とする分野
- 高硬度鋼(45 HRC以上)の加工
- 鋳鉄の高速加工
- 厳しい公差を必要とする仕上げ作業
CBNとPCBNの比較
多結晶立方晶窒化ホウ素(PCBN)は、CBN粒子をセラミックまたは金属バインダーで焼結したCBNの一種です。PCBNは純粋なCBNに比べて靭性が向上しており、断続切削加工やより多様な用途に適しています。
5.多結晶ダイヤモンド(PCD):非鉄のスペシャリスト
組成と特性
多結晶ダイヤモンド(PCD)は、ダイヤモンド粒子が金属バインダー(通常はコバルト)と一緒に焼結したものです。その結果、卓越した硬度と耐摩耗性を持つ素材となる。
メリットとデメリット
メリット
- 比類なき硬度と耐摩耗性
- 優れた熱伝導性
- 優れた表面仕上げ能力
- 適切な用途で長い工具寿命
デメリット
- 高コスト
- 高温における鉄系材料との化学反応性
- 脆いため、取り扱いや塗布に注意が必要
アプリケーション
PCD切削工具は理想的である:
- 非鉄金属(アルミニウム、銅、真鍮)の加工
- 研磨材(ガラス繊維、炭素繊維複合材)の切断
- 超精密機械加工
6.比較分析:サーメットインサート vs 超硬合金 vs CBN vs PCD
硬度比較
サーメットチップと超硬、CBN、PCDを比較する場合、硬度は非常に重要な要素です。最も柔らかいものから最も硬いものまで:
- カーバイド
- サーメット
- CBN
- PCD
PCDは最も硬度が高いが、鉄系材料では限界があるため、必ずしもすべての用途に最適な選択ではないことに注意することが重要である。
コスト比較
これらの切削工具材料のコストは大きく異なる。最も安価なものから最も高価なものまである:
- カーバイド
- サーメット
- CBN
- PCD
CBNとPCDの高いコストは、適切な用途では、その優れた性能と長い工具寿命によって正当化されることが多い。
さまざまな用途における性能
- サーメットチップ:鋼および鋳鉄の仕上げ加工に最適で、優れた表面仕上げを提供。
- 超硬:幅広い材料と作業に適した万能選手。
- CBN:硬化鋼や鋳鉄の加工、特に高速加工に優れている。
- PCD:非鉄および研磨材で比類のない性能を発揮。
7.よくある質問
CBNは超硬合金より硬いのですか?
はい、CBNは超硬よりもかなり硬いです。ヌープ硬度スケールでは、CBNは通常4000~5000KHNで、超硬合金は1000~2000KHNです。
CBNチップは何に使用されますか?
CBNインサート 主に焼入れ鋼(>45 HRC)、鋳鉄、その他の硬質材料の加工に使用されます。厳しい公差が要求される高速加工や仕上げ加工において優れた性能を発揮します。.
CBN砥石で超硬は削れますか?
はい、CBN砥石は超硬工具を効果的に研ぐことができます。CBNは非常に硬いため、超硬切削工具の研削と研磨に適しており、正確で耐久性のある刃先を提供します。
PCDとCBNはどう違うのですか?
PCDとCBNとの主な違いは以下の通り:
- 硬度:PCDはCBNより硬い
- 化学的安定性:CBNは鉄系材料を加工する場合、より安定性が高い。
- 用途PCDは非鉄や研磨材に優れ、CBNは焼き入れ鋼や鋳鉄に適している。
なぜCBNはPCDよりも鋼材加工に適しているのですか?
CBNは高温での化学的安定性が高いため、鋼の加工に適している。PCDは高温で鉄と反応しやすく、工具の摩耗を早める。CBNは安定性を保つため、焼入れ鋼や鋳鉄の効率的な加工が可能になる。
CBNはダイヤモンドより硬いのか?
いいえ、CBNはダイヤモンドより硬くはありません。ダイヤモンド(PCDを含む)は、既知の天然素材の中で最も硬いものです。しかし、CBNは2番目に硬い材料であり、特定の用途、特に鉄系材料の加工においては、ダイヤモンドよりも優れています。
CBNはなぜ高いのか?
CBNが高価なのは、いくつかの要因がある:
- 高温・高圧を伴う複雑な製造工程
- 自然発生は限られており、合成生産が必要
- 生産に必要な専門設備と専門知識
- ユニークな特性により、工業用途で高い需要
8.詳細な組成と物理化学的特性
サーメットチップ対超硬合金対CBN対PCDを比較する場合、各材料の詳細な組成と物理化学的特性を理解することが極めて重要です。この知識は、様々な加工用途における性能に関する洞察を提供します。
8.1 サーメット
構成:
- 硬質相:体積比で通常70~85%、炭化チタン(TiC)、炭窒化チタン(TiCN)、窒化チタン(TiN)から成る。
- 結合相:ニッケル、モリブデン、コバルトから成る。
物理化学的特性:
- 密度:5.6~7.4 g/cm³(組成による
- 硬度:1500-2200HV(ビッカース硬度)
- 熱伝導率: 15-40 W/m-K
- 熱膨張係数: 7.0-8.5 × 10-⁶/K
- 横方向の破断強度:1200~2500MPa
- ヤング率:400~450GPa
サーメットは、セラミックの高硬度と金属の靭性を併せ持ち、優れた耐摩耗性と熱安定性を提供します。チタンベースの硬質相が硬度と耐摩耗性を提供し、金属バインダーが靭性と耐熱衝撃性を向上させます。
8.2 超硬合金
構成:
- 硬質相:通常、体積比で70-97%、炭化タングステン(WC)から成る。
- 結合相:通常3~30%(体積比)、主にコバルト(Co
物理化学的特性:
- 密度:11.0~15.0 g/cm³(コバルト含有量による
- 硬度:1000-1800HV、コバルト含有量に反比例する。
- 熱伝導率: 50-100 W/m-K
- 熱膨張係数4.9-7.1 × 10-⁶/K
- 横方向の破断強度:1500~3000MPa
- ヤング率:450~650GPa
超硬チップは、硬度と靭性のバランスを提供します。超硬合金は耐摩耗性と硬度を提供し、コバルトバインダーは靭性と耐衝撃性を向上させます。超硬合金の粒径とコバルト含有量を変えることで、特性を調整することができます。
8.3 立方晶窒化ホウ素(CBN)
構成:
- CBN結晶:体積で50-95%
- 結合相:体積比で5~50%、典型的にはセラミック(TiN、AlNなど)または金属(Co、Ni、Alなど)
物理化学的特性:
- 密度3.4-4.3 g/cm³
- 硬度4000-5500 HV
- 熱伝導率: 100-200 W/m-K
- 熱膨張係数4.6-4.9 × 10-⁶/K
- 横方向の破断強度:500~800MPa
- ヤング率:680~720GPa
CBNは、ダイヤモンドに似た立方晶の結晶構造を持つ合成超硬材料です。特に鉄系材料の加工において、卓越した硬度、熱安定性、化学的不活性を発揮します。熱伝導率が高いため、加工中の熱放散が効率的です。
8.4 多結晶ダイヤモンド(PCD)
構成:
- ダイヤモンド結晶体積比90-95%
- 結合相:体積比5-10%、典型的にはコバルト
物理化学的特性:
- 密度3.5-4.0 g/cm³
- 硬度:8000~10000HV
- 熱伝導率: 500-2000 W/m-K
- 熱膨張係数: 2.0-4.8 × 10-⁶/K
- 横方向の破断強度:1200~1700MPa
- ヤング率:776~925GPa
PCDは、金属バインダー(通常はコバルト)と一緒に焼結されたダイヤモンド粒子で構成されています。比類のない硬度と耐摩耗性を備え、卓越した熱伝導性を併せ持つ。しかし、PCDは高温で鉄と化学反応するため、鉄系材料の加工には使用できない。
物理化学的特性の比較分析
サーメットインサート対超硬合金対CBN対PCDを評価する際、いくつかの重要な物理化学的特性が際立っている:
- 硬度:PCD > CBN > サーメット > 超硬合金この硬度順序は、研削加工における耐摩耗性と工具寿命に直接影響する。.
- 熱伝導率:PCD > CBN > 超硬合金 > サーメット高い熱伝導率により、加工時の放熱性が向上し、より高い切削速度が可能となる。.
- 密度:超硬合金 > サーメット > PCD > CBNCBNやPCDのような低密度材料は、高速回転工具において遠心力を低減する利点がある。.
- 熱膨張率:サーメット > 超硬合金 > CBN > PCD熱膨張係数の低い材料は、加工工程における温度変動時により優れた寸法安定性を維持する。.
- 横方向破断強度:超硬合金 > サーメット > PCD > CBN横方向破断強度が高いほど、欠けや破断に対する抵抗性が優れており、特に断続切削加工において重要である。.
これらの詳細な組成と物理化学的特性を理解することは、特定の加工用途に最適な切削工具材料を選択する際に極めて重要である。サーメットインサート対超硬合金対CBN対PCDの選択は、被削材、加工パラメータ、所望の結果との関連において、これらの特性を慎重に検討した上で行うべきである。
9.結論正しい切削工具材料の選択
サーメットインサート対超硬合金対CBN対PCDの議論において、万能の解決策はありません。その選択は、以下のような様々な要因によって決まります:
- 被削材
- 機械加工作業(荒加工、仕上げ加工、高速加工)
- 必要な表面仕上げ
- 工具寿命への期待
- 予算の制約
各材料のユニークな特性、利点、制限を理解することで、加工工程を最適化するための十分な情報に基づいた決定を下すことができます。CBNやPCDのような先端材料が特定の用途で優れた性能を発揮する一方で、超硬やサーメットチップのような伝統的な選択肢も、現代の機械加工では依然として重要な位置を占めていることを覚えておいてください。
機械加工技術が進化し続ける中、切削工具材料について常に情報を得ることは、業界における競争力を維持するのに役立ちます。一般的な鋼でもエキゾチックな合金でも、お客様のニーズに合った切削工具材料があります。